LATEST POSTS
Welcome to ElectricalExams.Co, this is the place for you if you want to learn the Basics of Engineering with Focus on Electrical and Electronics Engineering.
We have a large collection of Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) to help you refresh what you have learned in the school and will prepare you to the Engineering world in the Future.
Majority of the MCQs have been categorize for ease of learning and the questions came from actual Electrical and Electronic Board Exams across the Globe. It will hep you test your knowledge from Basic Mathematics to Basic Engineering lectures that’s is why we have provided lectures from all around the world.
To test your Engineering Knowledge we have collection of MCQs for Power Electronics, Power Systems, Transformers, Electrical Earthing, Electrical Wiring, Earth Resistance, Voltage and current Sources, Electric Drives, Synchronous Motor, Single Phase Induction Motor and More solve MCQs
We have solve MCQ’s for Electrical Engineering, SSC JE Topwise Papers, SCC JE 2009-2017, SCC JE 2018, SCC JE2019, UPPCL JE, DMRC JE
For the Basic of Electrical Engineering you can check our articles on Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering, Resistance temperature coefficients, Concept of Resistance and Ohm’s Law, Fundamental Quantities and Units, Resistors in Series, Parallel, Series Parallel
For Electrical machines we have basic of learnings for Transformers, DC Machines and Synchronous Machines.
For Electronic Engineering, to learn more, you can check our Electronic Devices lectures as well.
We have included on our learnings the People who have significant contributions to all Engineering Fields in Biography Sections.

Fundamental of Electrical Engineering | Concept Of Resistance and Ohm’s Law
Read More
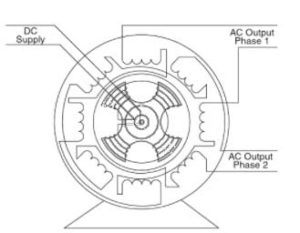
Working Principle Of An Alternator
Read More
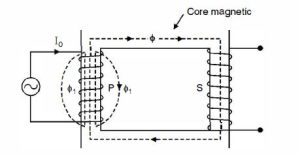
Ideal Transformer | Characteristics of Ideal Transformer
Read More

Fundamental Of Electrical Engineering
Read More
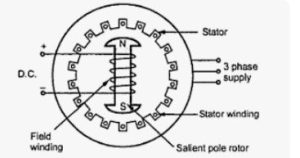
Working principle of synchronous motor
Read More
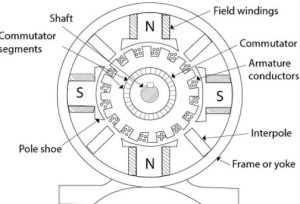
Working Principle of DC Motor
Read More

Leon Charles Thevenin – Biography, Contributions, Inventions
Read More

Georg Simon Ohm – Biography, Contributions, Inventions
Read More

Gustav Kirchhoff Biography, Contributions, Inventions
Read More