Ques 61. Which type of Motor is best suited for the excavator?
- DC Shunt Motor
- Differential Motor
- DC series Motor
- Synchronous Motor
Answer 3. DC series Motor Explanation:- The excavators are used for lifting or lowering a load. They are used for digging the ground hence the bucket connected to excavator always carry the heavy load such as soil, rock etc. For such application, high starting torque is required. In a DC series motor, the field winding and armature winding are in series connection. Since the flux produced is directly proportional to the armature current, torque is directly proportional to the square of the armature current. Thus more current is drawn than the DC shunt motor and hence more torque is produced.
Ques 62. Ward-Leonard controlled Direct current (dc) drives are generally used for
- Light Duty Excavator
- Heavy duty Excavator
- Medium Duty Excavator
- Any of the above
Answer. 2. Heavy Duty Excavator Ward Leonard control of dc machines is considered as one of the most elegant and efficient methods of speed control over a wide range. Check Question Number 2. for the full explanation. In early days the Ward Leonard control systems were used with the series motors but series motors need large contacts when turned from forward to reverse mode because there are large armature circuits that have to be opened when reversing the direction of rotation. To overcome the difficulties related to the series motors, separately excited dc-motors provide better performance to take the full control of the excavator as it improved the operating characteristics.The main advantages of Ward Leonard scheme are:
Ques 63. The contacts of the contactors are made up of
- Cadmium Copper
- Copper
- Silver
- All of the above
Answer. 4. All of the above Explanation:- A contactor is very similar to a relay except that a contractor contains large-load contacts designed to control large amounts of current. In the heating and air conditioning field, contactors are often used to connect power to resistance heater banks. Contactors may contain auxiliary contacts as well as load contacts. Materials used for making contacts operate under the severest conditions when the contacts make and break the electric circuit very frequently. When the contacts are separated, an arc is produced between the contacts ionizing the medium between the contacts. The contacts have to ~vithstand arcing or sparkover. The contact is damaged with time due to corrosion from oxidation and erosion from fusing. Classification of the contactors Depending upon the power level of the circuit, to contact materials are classified as “lightly” and “moderately” loaded when the current does not exceed 1 A and the voltage causing the arc is of the order 10 to 20 V. At higher power levels, the materials are classified as “heavily loaded”. Contacts operate more satisfactorily in the vacuum that in a gaseous medium due to the reason that vacuum eliminates arc between the electrodes. An important property of the materials used for contact is the stability of “Contact resistance”. The following materials are used rot making the contacts depending upon the power level of the electric circuit. Lightly Loaded Contacts: They are made from the pure noble metals such as platinum, palladium, gold, and silver. The alloy of platinum with iridium is used for making contacts of very high reliability. Silver or its alloys with copper are the commonly used materials for the contacts. Rhodium also is an excellent contact material. Tungsten and molybdenum are also in use because of the high cost of noble metals. Non-arcing contacts are made by electro-deposition of platinum, gold, silver, palladium or rhodium on springs and contact surfaces thus reducing the cost Without loss in efficiency. Metals for heavily loaded contacts:- The operating condition of the heavily loaded contact is 500V. The materials used for heavily loaded contacts are discussed below:
Ques 64. Which type of electromagnet is preferred for noiseless operation?
- AC electromagnet
- DC electromagnet
- Both AC and DC electromagnets
- None of the above
Answer 2. DC electromagnets Explanation:- Electromagnets use electricity to create their power of magnetism. Electricity moving along the straight wire creates a magnetic field. This magnetic field gets weaker as it moves away from the wire. But if the wire is coiled, the magnetic field is forced back toward the wire and it becomes stronger. Electromagnets are made of coils of wire called as solenoids. DC Motor Pros: DC Motor Cons AC Motor Pros AC Motor Cons
Ques 66. For the high-frequency choppers, the device that is preferred is
- TRIAC
- Thyristor
- Transistor
- GTO
Answer 3. Transistor Explanation:- A chopper is a static power electronic device that converts the fixed dc input voltage to a variable dc output voltage. It is also known as the DC-DC converter. Control of a d.c. motor’s speed by a chopper is required where the supply is d.c. (as from a battery) or an a.c. the voltage that has already been rectified to a d.c. voltage. The most important applications of choppers are in the speed control of d.c. motors used in industrial or Faction drives. Choppers are used for the control of d.c. motors because of a number of advantages, such as high efficiency, flexibility in control, lightweight, small size, quick response, and regeneration down to very low speeds. Chopper controlled d.c. drives have also applications in servos in battery operated vehicles such as forklift trucks, trolleys etc. The choppers offer a number of advantages over controlled rectifiers for a dc. motor control in open-loop and closed-loop configurations. Because of the higher frequency of the output voltage-ripple, the ripple in the motor armature current is less and the region of discontinuous conduction in the speed-torque plane is smaller. A reduction in the armature current ripple reduces the machine losses and its aerating. A reduction or elimination of discontinuous conduction region improves speed regulation and transient response of a drive. To realize a higher frequency of output voltage ripple, it is customary to use a rectifier with a higher pulse number. Use of a rectifier with a higher pulse number results in a low utility factor for thyristors and a relatively high cost. On the other hand, a chopper can be operated at comparatively high frequencies. For example, it is possible to operate a chopper at 300 Hz even with converter grade thyristors. With inverter-grade thyristors, the frequency can be increased to 600 Hz. If the output voltage range can be lowered, corresponding frequencies can be increased to 400 Hz and 800 Hz, respectively. When power transistors are employed, frequencies can be higher than 2.5 kHz. For low power applications, power MOSFET can be used and the frequency can be higher than 200 kHz. The rectifier output voltage and current have a much lower frequency, 100 Hz in the case of a single-phase rectifier and 300 Hz in the case of a three-phase fully controlled rectifier when the a.c. source frequency is 50 Hz. Summary:- Where high power is involved, an SCR is used as the switch whereas, in medium and low power applications, a transistor is the most suitable.
Ques 67. According to the rated duty of the contactors, the number of operations per hour in case of will be around
- 100
- 600
- 1200
- 2000
Answer. C. 1200 Explanation:- The rated duty of the contactors is defined as the number of duty cycles ranging from uninterrupted duty (contactor closed for an indefinite period) to an intermittent duty of 1,200 operating cycles per hour.
Ques 68. In case of contactors, the duty in which the main contacts remain closed for a period bearing a definition in relation to the no-load periods is known as
- Intermittent Duty Cycle
- Short Time Duty Cycle
- Temporary Duty Cycle
- Uninterrupted Duty Cycle
Answer. 1. Intermittent Duty Cycle Explanation:- Intermittent duty Class. A duty in which the main contacts of a contactor remain closed for periods bearing a finite relationship to the no-load periods, both periods being too short to allow the contactor to reach thermal equilibrium. The intermittent duty above implies a capability of operation at a rate of 12 operating cycles per hour, the on-load period of each cycle being 60% of the whole cycle. Starting and braking are not taken into account on the assumption that the times taken up by these events are too short in comparison with the on-load period, and therefore do not appreciably affect the heating of the motor. The load torque during one cycle may be greater than the rated torque of the motor. The load torque during one cycle may be greater than the rated torque of the motor. When stating the motor power for this form of duty, it is also necessary to state the cyclic duration factor: cyclic duration factor = (on time/cycle time) x 100% The standards specify that the duration of one cycle must b shorter than 10 min. Cases, where the duty cycle is longer than 10 min, must be brought to the attention of the motor manufacturer.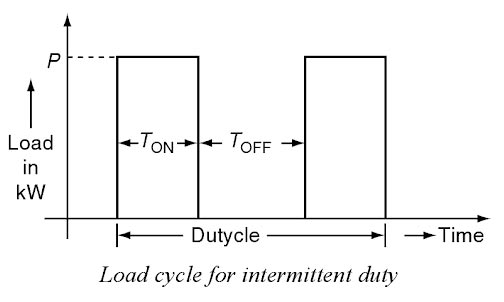
Ques 69. In the case of the contactors, the ratio of the service period to the entire period is known as
- Duty
- Load Factor
- Class of the contacts
- None of the above
Answer 3. Class of the contacts Explanation:- In contactors, the ratio of the service period to the entire period is known as the Load factor.
Ques 70. A class 1 contactor should be mechanically sound to withstand
- 0.05 million times
- 0.025 million times
- 0.1 million times
- 10 million times
Answer. B. 0.025 million times Explanation:- Mechanical endurance:- 1 million no-load operating cycles. This represents the number of no-load operating cycles which can be made before it becomes necessary to service or replace any parts other than contacts. Duty Class 1:- For use in systems where the power factor of short-circuit current is extremely low, e.g., where the switchgear is connected in relatively close proximity to the source of generation. Duty Class 1 is the normal or medium requirement contactors. For MV contractors such minimum requirements might be specified as:



