Which of the following material will be preferred as a shunt for extending the range of measurement of a voltmeter?
Right Answer is:
Manganin
SOLUTION
Manganin material is preferred as a shunt for extending the range of measurement of a voltmeter.
The range is the maximum value of the measurement that can be measured by a given meter. The range of voltmeters, ammeters, etc., is limited by the current-carrying capacity of the control springs, high measuring parameters, etc. Thus, for the measurement of large current and voltage values, it is necessary to employ a device that reduces the current and voltage of the instrument by a known proportion.
Shunts are small resistances connected in parallel to increase the range of an ammeter. For multi-range ammeters, the moving coil remaining the same; separate shunts are used to increase the range of measurement of a single instrument.
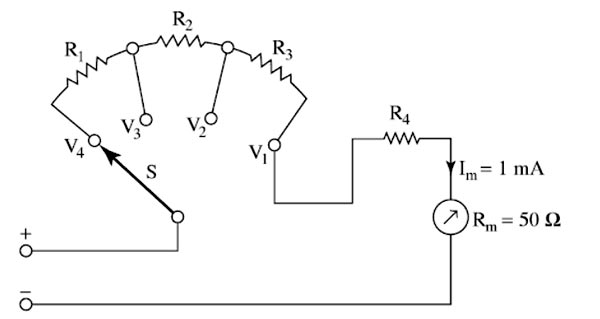
To extend the current-measuring capabilities of the meter movement it is necessary to connect a resistor in parallel with the coil. This causes the current that is to be measured to divide, a small part flowing through the coil and the remainder passing through the shunt resistor. The wire from which the coil is made is nearly always copper; unfortunately, the resistance of a copper coil varies appreciably with temperature. A shunt resistor is then used whose resistance is practically constant over the operating temperature range; this guarantees a constant ratio between the coil resistance and the shunt resistance.
Manganin is the usual alloy used for shunts because this material has a negligible temperature coefficient at the temperatures involved. There is also a negligible thermoelectric effect when manganin is used with copper.
