How should a fuse be installed in a circuit to ensure proper operation?
Right Answer is:
Series with the load
SOLUTION
A fuse wire is connected in series in the electric circuits so that current flowing through the conductor to any load must also pass through the fuse.
Fuse is the current interrupting device that breaks or opens the circuit (in which it is inserted) by fusing the elements when the current in the circuit exceeds a certain value.
Fuse is the simplest and cheapest device used for interrupting an electrical circuit under the condition of short-circuiting, or excessive overload, current magnitudes.
A fuse is a safety device having a short length of a thin, tin-plated copper wire having a low melting point, which melts and breaks the circuit if the current exceeds a safe value. The thickness and length of the fuse wire depend on the maximum current allowed through the circuit. An electric fuse works on the heating effect of current. The fuse for protecting our domestic wiring is fitted just above our main switch on the switchboard.
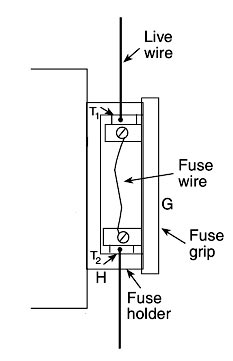
The main fuse in domestic wiring consists of a porcelain fuse holder H having two brass terminals T1 and T2 in it. This is connected in the live wire. The other part of the fuse is a removable fuse grip G which is also made of porcelain. The fuse grip has a fuse wire fixed in it. When fuse grip is inserted in the fuse holder as shown in Figure, then the circuit of our domestic wiring is completed. So, under normal circumstances when the current is within the limit, then the fuse wire is intact and electric current is available in our wiring.
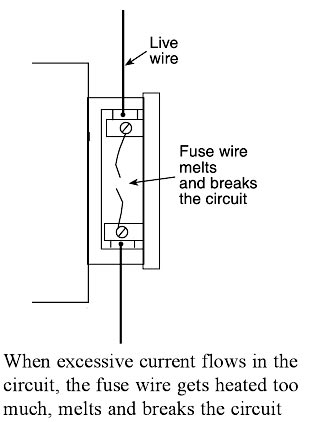
When a short circuit takes place, or when overloading takes place, the current becomes large and the fuse wire too much. Since the melting point of fuse, wire is much lower than copper wires, the fuse wire melts and breaks the circuit as shown in Figure. When the fuse wire breaks, the electricity supply is automatically switched off before any damage can be done to the rest of the wiring (or the electric appliances being used).
We will now give some important points about the fuse wire to be used in electrical circuits. First of all, we should know why we use a thin wire as a fuse wire and not a thick wire. We use a thin wire in a fuse because it has a much greater resistance than the rest of connecting wires. Due to its high resistance, the heating effect of current will be much more in the fuse wire than anywhere else in the circuit. This will melt the fuse wire whereas other wirings will remain safe. We should not use a thick wire as a fuse wire because it will have low resistance and hence it will not get heated to its melting point easily. The fuse wire is usually made from tin-plated copper wire having a low melting point so that it may melt easily. A pure copper wire cannot be used as a fuse wire because it has a high melting point due to which it will not be easy when a short circuit takes place.
Fuse wire is made with an alloy of lead and tin having a low melting point and low resistance (although the resistance of fuse wire is higher than that of electrical appliances). If due to any malfunction or fault, excessive current begins to flow through the circuit, the fuse wire immediately melts due to the heat generated by the flowing current. The circuit is broken and the excess current, which may damage equipment is prevented from flowing.
It is used for Overload and for short-circuit protection in high voltage (upto 66 kV) and for low Voltage (upto 120 V – 240 V) installations/circuits.
Characteristics of a fuse are:-
- It should have a low melting point.
- It should have low ohmic losses.
- It should have high conductivity. ( or low resistivity)
- It should be economical.
- It should be free from detraction.
