Ques.21. Arc blow is a welding defect that is encountered in
- Arc welding using D.C current
- Arc welding using A.C current
- Gas welding
- Thermit welding
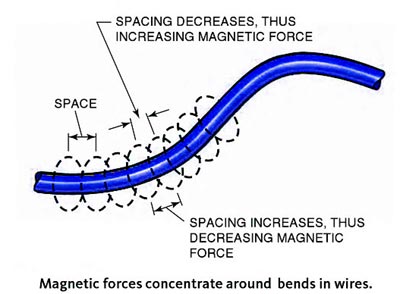
Answer.1. Arc welding using D.C current Explanation:- When electrons flow, they create lines of magnetic force that circle around the path of flow. These lines of magnetic force are referred to as magnetic lines of flux. They space themselves evenly along a current-carrying wire. If the wire is bent, the flux lines on one side are compressed together, and those on the other side are stretched out, as shown in Figure. The unevenly spaced flux lines try to straighten the wire so that the lines can be evenly spaced once again. The force that they place on the wire is usually small, so the wire does not move. However, when welding with very high amperages, 600 amperes or more, the force may actually cause the wire to move. The welding current flowing through a plate or any residual magnetic fields in the plate results in unevenly spaced flux lines. These uneven flux lines can, in turn, cause the arc between the electrode and the work to move during welding. The term arc blow refers to this movement of the arc. Arc blow makes the arc drift like a string would drift in the wind. Arc blow can be more of a problem when the magnetic fields are the most uneven such as when they are concentrated in corners, at the ends of plates, and where the work lead is connected to only one side of a plate. The more complex a weldment becomes, tt more likely arc blow will become a problem. Comply weldments can distort the magnetic lines of flux in unexpected ways. If you encounter severe arc blow during a weld, stop welding and take corrective measures to control or reduce the arc blow. Arc blow can be controlled or reduced by connecting the work lead to the end of the weld joint and then welding away from the work lead, Another way of controlling arc blow is to use two work leads, one on each side of the weld. The best way to eliminate arc blow is to use an alternating current. AC usually does not allow the flux lines to build long enough to bend the arc before the current changes direction. If it is impossible to move the work connection or to change to AC, a very short arc length can help control arc blow. A small tack weld or a change in the electrode angle can also help control arc blow.ARC BLOW
Ques.22. A rectifier for welding has voltage/current characteristics as
- Drooping
- Rising
- Static
- Variable
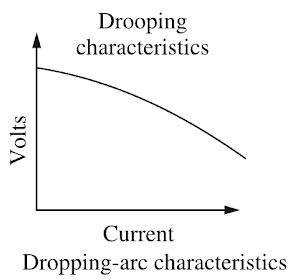
Answer.1. Drooping Explanation:- Rectifier for welding consists of a transformer (single-or three-phase) and a rectifier unit as shown in Fig. Such a unit has no moving parts, hence it has a long life. The only moving part is the fan for cooling the transformer. But this fan is not the basic part of the electrical system. Fig. shows a single-phase full-wave rectifier circuit of the welder. Silicon diodes are used for converting a.c. into d.c. These diodes are hermetically sealed and are almost ageless because they maintain rectifying characteristics indefinitely. Such transformer-rectifier welding is most adaptable for shied arc welding because it provides both d.c. and a.c. polarities. It is very efficient and quiet in operation. These welders are particularly suitable for the welding of The open-circuit voltage of a constant-current, rectifier type power source ranges from about 50 to 100 V hence it provides the highest potential voltage when the welding current circuit is open and no current is flowing. At the start of the weld, with striking the arc, the sharp drop in voltage takes place from the OCV. A conducting column of ionized gases is formed along with the heating up of the electrode. As there is a drop in voltage, the simultaneous increase in welding current takes place. After a certain point, the voltage/current variation becomes linear following Ohm’s law. The static volt-ampere characteristics of a welding power source are shown in Fig. 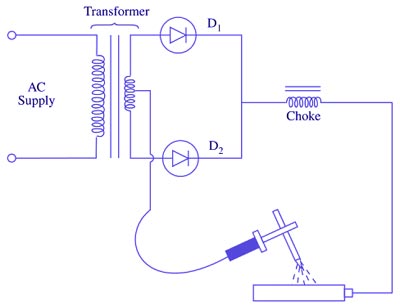
Ques.23. The advantages of welding motor-generator are
- Easily Portable
- Used for ferrous and Non-ferrous material
- Can be used for all welding position
- Less maintenance
Answer.4. Less maintenance Explanation:- Motor generator power source consisting of an electric motor coupled to a generator or alternator that produces the desired welding power. These machines produce superior weld qualities. However, due to the moving parts, they require frequent maintenance. Welding generators can be of both AC and DC type. The electric motor provides a good constant-speed drive for the generator and is not affected by the load imposed upon it. The generator is specially designed for welding purposes so that it generates about 60 volts on an open circuit; this drops to about 20 volts immediately after the arc is struck. Generators are built in various current ratings ranging from about 100 to 600 amperes, and most modern types incorporate means for automatically adjusting the voltage to meet variations in the demand of the arc Although the arrangement of the control unit may vary for machines made by different manufacturers, most consist of a wheel or lever control which selects the correct current for the right size of electrode and thickness of plate being welded. DC generators usually have a polarity switch which enables the welder to reverse the polarity, as is occasionally required when welding with special electrodes. Such a d.c. the welder has the following advantages: Disadvantages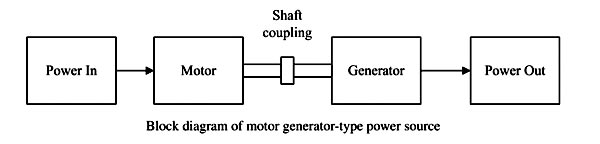
Ques.24. For welding duty rectifiers commonly used are
- Mercury arc rectifier
- Selenium metal rectifier
- Any of the above
- None of the above
Answer.2. Selenium metal rectifier
Explanation:-
Welding rectifiers:-
Welding rectifiers change AC current into DC current and may be used as a power source for various arc welding processes, depending on the machine. Some Shielded metal arc welding (SMAW) machines have built-in welding rectifiers so that the welding current output is more stable. Rectifiers have a constant-current control where the total power output stays the same while the machine is being used, depending on how the machine has been set. If more amps are needed, then the power output will change when the controls are reset.
Type of Rectifier used in welding
- Selenium rectifier
- Silicon Rectifier
The selenium rectifier is also known as the metal rectifier. The selenium rectifier is an early type of semiconductor rectifier in which the semiconductor is a copper oxide or selenium. This device is used in phase-controlled converters, inverters, battery chargers, and cyclo-converters and welding purposes. At the end of the 1950s static welding rectifiers were introduced. Selenium rectifiers were used initially followed later by silicone rectifiers.
It consists of an Iron or aluminum base disc coated with selenium, which is a non-metallic element of atomic number 34. A coating of an alloy of tin, cadmium, or bismuth is deposited onto the selenium and forms the counter-electrode
A current will flow from disc to counter-electrode but not in the reverse direction in which a high resistance is offered so that the unit acts as a rectifier. To increase the current-carrying capacity the disc is made larger in area and units are connected in parallel. For higher voltages units are connected in series since, if the voltage drop across the unit is too high, the reverse current increases rapidly and the rectifier fails.
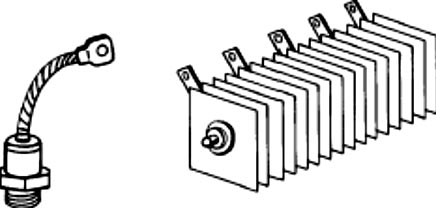
Today silicon diode rectifiers are preferred to selenium or germanium rectifiers, because they have greater rectification efficiency and, are not Rippled by aging as the latter types are. Silicon diodes are smaller than selenium diodes and are hermetically sealed and mounted on a suitable fan for cooling.
Note:-
A mercury-arc rectifier or mercury-vapor valve is a type of electrical rectifier which is used to convert high ac voltage into DC voltage. They were very useful to provide power for industrial motors, electric railways, and electric locomotives, as well as big voltage direct current (HVDC) power transmission.
At the lower voltages required for arc welding, the mercury arc rectifier is less efficient because of its almost constant voltage drop
Ques.25. In resistance welding, aluminum, as compared to steel, requires
- Larger welding time
- Smaller welding time
- Equal welding time
- Welding time depends upon the value of weld current
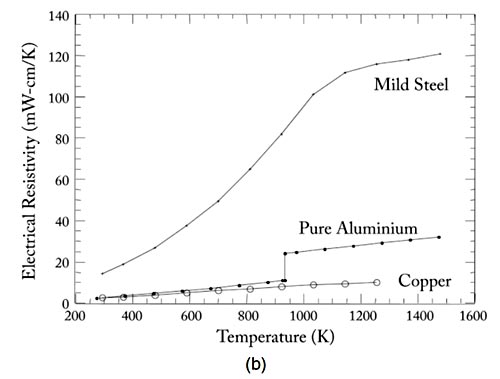
Answer.2. Smaller welding time Explanation:- The resistance welding is applicable to both steel and aluminum. As indicated in Figure, the dynamic resistance curve for aluminum is entirely different from the curve for steel. Two facts contribute to this vast difference the oxide on the surface of the aluminum and the small change in resistivity as a function of temperature. Upon initial flow of current, resistances are extremely high due to the oxide layer that has a much higher resistivity than aluminum. This increases the likelihood of initial expulsion, and will also result in significant electrode heating. The oxide layer quickly breaks down allowing current to pass more easily as resistance drops rapidly. However, as compared to the dynamic resistance curve for steel, there is no significant increase in resistance later in the cycle. The reason for this is compared to steel, aluminum’s resistivity increases only slightly with temperature, as shown in Figure (b). The implication of this difference is that there is limited opportunity to grow the nugget by taking advantage of the rapid increase in resistivity as is the case with steel. This is one of the fundamental reasons why aluminum spot weld times need to be much shorter than those of steel.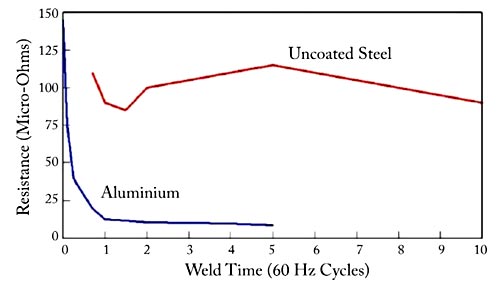
Ques.26. Which of the following is not a welding accessory?
- Electrode holder
- Work Clamp
- Cable
- Gloves
Answer.4. Gloves Explanation:- A number of items must be used with a welding machine to complete the setup. The major items are the welding cables, the electrode holders, and the work clamps. Welding Cables:- Welding cables are conductors to carry current throughout the welding operation. Two electrode cables are necessary to connect the electrode and workplace to the welding power source. These cables must be insulated with rubber and need a periodic inspection for the proper welding operation. Electrode holder:- It is a device used to insert or hold the electrodes for carrying out the welding operation. Electrode jaws used to hold the electrode in the holder must be completely insulated against thermal and electric shocks. Electric holders must be mechanically strong. Work Clamps:- The work clamp must be the correct size for the current being used, and it must clamp tightly to the material. Heat can build up in the work clamp, reducing welding efficiency, just as was previously described for the electrode holder. Power losses in the work clamp are often overlooked. The clamp should be touched occasionally to find out if it is getting hot.
Ques.27. Chipping hammers are used
- To remove slag from welding
- To align the pieces to be welded
- For tage welding
- For marking spots to be welded
Answer.1. To remove slag from welding Explanation:- Chipping hammer and wire brush A chipping hammer is a chisel-shaped device that is used to remove the slag formed over the molten weld. A chipping hammer is necessary for the removal of protective slag over a molten welded bead tip. After the weld has solidified and is relatively cooler, you can remove the slag protection. This is accomplished with a chipping hammer. The chipping hammer normally has a pointed end and a chisel-like end. The hammer cracks the slag, thus allowing it to peel away and expose the welded bead. When using a chipping hammer, you must wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from the hot slag. Protective clothing (apron, gloves, etc.) is necessary to protect the welder from the hot spattering particles, against thermal shocks, etc.
Ques.28. The welding electric circuit is
- Always earthed
- Never earthed
- Through cables only
- None of the above
Answer.1. Always earthed Explanation:- General safety in Welding Generally, welding and thermal cutting operations are not hazardous but a completely safe workplace. Safety is necessary for welding because electric current or high voltage current is used in it. The hazards which are more or less peculiar to welding are: Electric Shock Electric shock may occur in welding if current happens to pass through the welder’s body. The magnitude of the content will depend on the resistance offered by the body. A current of 0.1 A or above, be it a.c. or d.c. is taken to be lethal to humans. Since the maximum human body resistance is 600 ohm, the lethal current will be provided by the voltage of just 60 V (V = i R). Electric shock results in many accidents that occur during welding. Therefore necessary precautions must be taken to minimize electric shock. This can best be done by ensuring proper insulation of cables, and reliable earthing of welding equipment. The grounding circuit sanitary sewers and water pipes or metallic structures of buildings and process equipment should never be used as earth or returned for welding circuit.
Ques.29. The eyes of the welding operator must be protected against
- Ultraviolet radiation
- Infrared radiations
- Both (A) and (B)
- Solar radiation
Answer.3. Both (A) and (B) Explanation:- Burns Caused by Light Some types of light can cause burns. There are three types of light—ultraviolet, infrared, and visible. Ultraviolet and infrared are not visible to the unaided human eye but can cause burns. During welding, one or more of the three types of light may be present. Arc welding and arc cutting produce all three kinds of light, but gas welding produces only the less hazardous visible and infrared lights. Ultraviolet Light (UV) Ultraviolet light waves are the most dangerous. These can cause first-degree and second-degree burns to the eyes or to any exposed slain. Because you cannot set or feel ultraviolet light while being exposed to it, you must stay protected when in the area of any arc welding processes. The closer a person is to the arc ant the higher the current, the quicker a burn may occur. The ultraviolet light is so intense during some welding processes that eyes can receive a flash burn within seconds, and the skin can be burned within minutes. Ultraviolet light can pass through loosely woven clothing, thin clothing, light-colored clothing, and a damaged or poorly maintained arc welding helmet. Infrared Light Infrared light is the light wave that is felt as heat. Although infrared light can cause burns, a person will immediately feel this type of light. Therefore, burns can easily be avoided. Visible Light Visible light is the light that we see. It is produced in varying quantities and colors during welding. Too much visible light may cause temporary night blindness (poor eyesight under low light levels). Too little visible light may cause eyestrain, but visible light is not hazardous. Whether burns are caused by ultraviolet light or hot material, they can be avoided if proper clothing and other protection are worn. Face and Eye Protection Eye protection must be worn in the shop at all times. Eye protection can be safety glasses with side shields, goggles; or a full face shield. For better protection when working in brightly lit areas or outdoors, some welders wear flash glasses, which are special, lightly tinted safety glasses. These safety glasses provide protection from both flying debris and reflected light.
Ques30. The danger of electric shock is maximum
- During arcing
- After arcing
- Before welding
- While inserting an electrode into the holder
Answer.4. While inserting an electrode into the holder Explanation:- Electric shock is one of the most serious and immediate risks facing a welder. Electric shock can lead to severe injury or death, either from the shock itself or from a fall caused by the reaction to a shock. Causes of electric shock Protection from electric shock



