H.R.C. fuses provide the best protection against
Right Answer is:
Short-circuits
SOLUTION
HRC Fuses
High rupturing capacity (HRC) Fuse links provide complete protection to cables, switchgear, control gear, and other equipment by limiting the current, both in magnitude and in the time duration, that can pass through these devices in the circuit. It is always desirable to protect a power circuit against short circuits separately. HRC fuses are the immediate answer to such a requirement for small and medium-sized LV motors. They have a delayed action characteristic under an over-load and are instantaneous against a shortcircuit condition and thus inherit the quality of discrimination. They reduce the electromagnetic and thermal stresses and enhance the withstand capacity of the Protected equipment for higher fault levels.
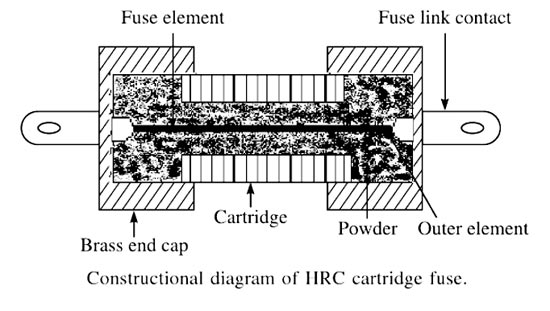
These type of fuses comprises a high-grade ceramic body within which fuse elements are placed and welded to the endplates. The assembly is filled with dry granular quartz sand. In the event of flow of high short circuit current, this quartz sand solidifies forming high resistance glass in the arc path to ensure effectively are quenching in optimum time. The fuse elements are the non-deteriorating type which means that they maintain their characteristics over the long service period.
The fuse element is either pure silver or bimetallic in nature. Silver-plated tag contacts provide good contact with fuse base and keep the fuse temperature low. These types of fuses can be plugged in and out even when hot or in service with an insulated fuse puller. The fuse element in the form of a long cylindrical wire is not used because after melting, it will form a string of droplets and an arc will be struck between each of the droplets. The shape of the fuse element depends upon the characteristic desired.
When the fuse carries a normal rated current, the heat energy generated is not sufficient to melt the fuse element. But when a fault occurs, the fuse element melts before the fault current reaches its first peak. As the element melts, it vaporizes and disperses.
Advantages of HRC Fuses
- The capability of clearing high values of fault currents
- Fast operation
- Non-deterioration for long periods
- No maintenance needed
- Reliable discrimination
- Consistent in performance
- Cheaper than other circuit interrupting devices
- Current limitation by cut-off action
- Inverse time-current characteristic
Disadvantages of HRC Fuses
- It requires replacement after each operation.
- Inter-locking is not possible.
- It produces overheating of the adjacent contacts.
Applications of HRC Fuses
- Protection of low voltage distribution systems against overloads and short-circuits.
- Protection of cables
- Protection of busbars
- Protection of motors
- Protection of semiconductor devices
- Back up protection to the circuit breaker
