Ques.21. The Principle of the Simple photometer is based upon
- Inverse Square Law
- Square Law
- Inverse Law
- Lambert cosine Law
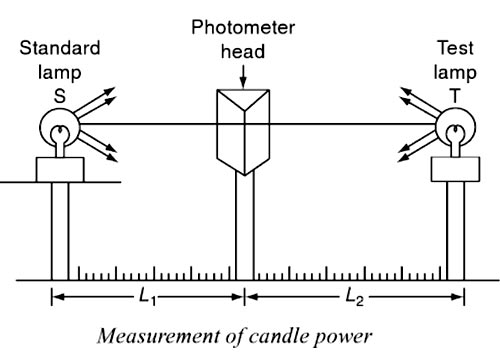
Answer.1. Inverse Square Law Explanation:- Photometry involves the measurement of candlepower or luminous intensity of a given source. The photometer bench essentially consists of two steel rods Invite 2- to 3-m long. This bench carries stands or saddles for holding two sources (test and standard lamps), the carriage for the photometer head, and any other apparatus employed in making measurements. The photometer bench should be rigid so that the source being compared may be free from vibration. The photometer head should be capable of moving smoothly and the photometer head acts as the screen for the comparison of the illumination of the standard lamp and the test lamp. The principal methods of measurement arc based upon the inverse square law. The photometer bench consists of two sources, the standard source “S” whose candlepower is known, and the other source ‘T’ whose candlepower is to be determined. The photometer head acts as the screen is moved in between the two fixed sources until the illumination on both sides of the screen is the same. A simple arrangement for the measurement of the candlepower of the test source is shown in Fig. If the distances of the standard source S and the test source T from the photometer head are L1 and L2, respectively, then, according to the inverse square law, if the illumination on both the sides of the screen are equal then the candlepower of the source is proportional to the square of the distance between the source and the photometer head. The CP of standard source ∝ L12 The CP of test source ∝ L22 ∴ CP of test source ⁄ CP of standard source = L22⁄ L12 CP of test source = S × L22⁄ L12 In order to obtain the accurate candlepower of the test source, the distance of the sources from the photometer head should be measured accurately.The principle of simple photometer
Ques.22. Two electric bulbs have tungsten filament of the same thickness. If one of them gives 60 W and the other gives 100 W, then
- 60W and 100 W lamp filaments have equal length
- 60 W lamp filament has a shorter length
- 100 W lamp filament has the longer length
- 60 W lamp filament has the longer length
Answer.4. 60 W lamp filament has the longer length Explanation:- Let’s suppose the voltage is the same for both the bulb Power P = V2/R P = V2A/ρl………………. (since specific resistance R= ρ (L/A). L =V2A/ρP Since both, the filament has the same thickness. So ‘A’ voltage will be the same l ∝ 1/P Hence Filament of low power will have a longer length. Note:- If P ↑ R↓ L ↓ For a more watt bulb, less resistance will be there so, the length of that bulb will be lower.
Ques.22. Light is produced in electric discharge lamps by
- Heating effect of current
- Magnetic effect of current
- Ionization in a gas or vapor
- Carbon electrodes
Answer.3. Ionization in a gas or vapor Explanation:- In all discharge lamps, an electric current is made to pass through a gas or vapor, which produces its illuminance. Normally, at high pressures and atmospheric conditions, all the gases are poor conductors of electricity. But on the application of sufficient voltage across the two electrodes, these ionized gases produce electromagnetic radiation. In the process of producing light by gaseous conduction, the most commonly used elements are neon, sodium, and mercury. The wavelength of the electromagnetic radiation depends upon the nature of gas and the gaseous pressure used inside the lamp. A simple discharge lamp is shown in Fig. The production of light in the gaseous discharge lamps is based on the phenomenon of excitation and ionization of gas or metal vapor present between the two electrodes of a discharge tube. When the potential between the two electrodes is equaled to ionizing potential, gas or metal vapor starts ionizing and an arc is established between the two electrodes. Volt-ampere characteristics of the arc are negative, i.e., gaseous discharge lamp possesses negative resistance characteristics. A choke or ballast is provided to limit high currents to a safe value. Here, the choke serves two functions. The use of choke will reduce the power factor (0.3-0.4) of all the gaseous lamps so that all the discharge lamps should be provided with a condenser to improve the power factor. The nature of the gas and vapor used in the lamp will affect the color affected by light.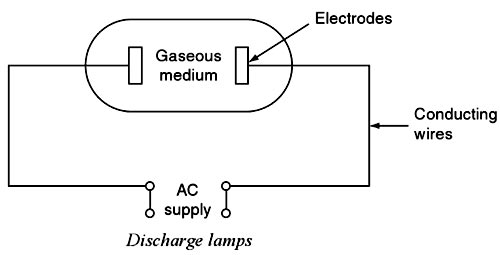
Ques 23. The color of the light given out by a sodium vapor discharge lamp is
- Pink
- Bluish Green
- Yellow
- Blue
Answer.3. Yellow Explanation:- A sodium-vapor lamp is a gas-discharge lamp that uses sodium in an excited state to produce light at a characteristic wavelength near 589 nm. There are two varieties of such lamps: low pressure and high pressure. Low-pressure sodium lamps are highly efficient electrical light sources, but their yellow light restricts applications to outdoor lighting such as street lamps. High-pressure sodium lamps produce a broader spectrum of light than low-pressure lamps, but they still have poorer color rendering than other types of lamps. Low-pressure sodium lamps only give monochromatic yellow light and so inhibit color vision at night.
Ques.24. Lumen/watt is the unit of
- Light Flux
- Luminous Intensity
- Brightness
- Luminous Efficiency
Answer.4. Luminous Efficiency Explanation:- The luminous efficiency of an electric lamp is the ratio of the luminous flux (in Lumen) emitted by the lamp to the electric power (in watt) given to it i.e η = Luminous flux (in Lumen) emitted by the lamp ⁄ Electric power (in watt) It is clear that the luminous efficiency of the electric lamp is measured in Lumen/Watt
Ques.25. The S.I unit of Luminance is
- Candela
- Lux
- Candela/m2
- m2/candela
Answer.3. Candela/m2 Explanation:- Luminance describes the rate at which visible light is emitted from a surface (lightbox) or display device (CRT or flat panel display). or The intensity of the light emitted in a given direction by the unit area of a luminous or reflecting surface. It is the luminous flux emitted in the given direction from a surface element, divided by the product of the projected area of that element perpendicular to the prescribed direction and the solid angle containing the direction. It is expressed The SI unit for luminance describing the energy of visible light is the lumen-second and the unit for luminance is 1 lumen per steradian per m2; this is the candela per m2 (Candela/m2) or sometimes referred to as a ‘nit’
Ques.26. Which gas is sometimes used in filament lamps?
- Argon
- Krypton
- Nitrogen
- Carbon dioxide
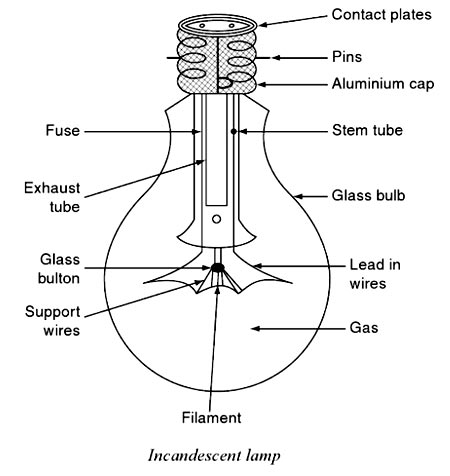
Answer.1. Argon Explanation:- These lamps are temperature-dependent sources. When an electric current is made to flow through a fine metallic wire, which is known as the filament, its temperature increases. At low temperatures, it emits only heat energy, but at very high temperatures, the metallic wire emits both heat and light energy. These incandescent lamps are also Blown as temperature radiators. Choice of material for the filament The materials commonly used as the filament for incandescent lamps are carbon, tantalum, tungsten, and osmium. The materials used for the filament of the incandescent lamp have the following properties. The color temperature of a normal filament lamp is typically between 2800 K and 3000 K. At the extremely high temperature of the filament, tungsten tends to evaporate. This leads to the familiar blackening of an incandescent lamp envelope. The evaporation of the tungsten filament can be reduced by filling the lamp envelope with a suitable gas that does not chemically attack the filament. However, gases also cool the filament by conducting heat away from it, and they decrease lamp efficiency. The gas used must, therefore, be carefully chosen. It should adequately suppress tungsten evaporation without overcooling the filament. In addition, it should not readily pass an electric current, for otherwise arcing may occur which would destroy the lamp. Argon and nitrogen are the gases most commonly used. Nitrogen will minimize the risk of arcing but will absorb more heat than argon. Argon is used by itself in general service lamps. A mixture of the two gases is used in incandescent lamps where the tendency for arcing is more likely, such as in projector lamps. In this case, the amount of nitrogen present is kept very small as little as 5% in order to obtain optimum lamp efficiency. Lamps filled with krypton gas have a longer life than argon and nitrogen lamps and cost more.INCANDESCENT FILAMENT LAMP
Ques.27. Which bulb operated on the lowest power?
- Night Bulb
- Neon Bulb
- GLS Bulb
- Torch Bulb
Answer.4. Torch Bulb Explanation:- The small electric bulb which produces light when a torch is switched on is called a ‘torch bulb’. The torch bulb consists of a small glass bulb fixed on a metal case. Inside the glass bulb, there is a very ‘thin wire’ fixed between two thick wires. The thin wire inside the bulb is called the filament of the bulb. The filament is usually made of a very thin tungsten wire. It is the filament of the bulb which glows when electricity from a cell is passed through it. Torches operate on batteries which generally provide just a few (typically 1.5–6 V) volts DC, and because of the limited capacity (in mAH) of those batteries, flashlight bulbs typically consume fractions of a watt (W) to several watts of power at most, which in turn limits the light output/illumination they can provide. 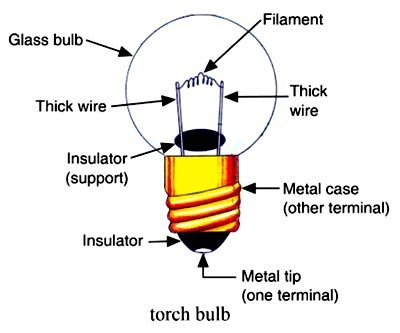
Ques.28. The output of a tungsten filament lamp depends on
- Size of lamp
- Size of shell
- Temperature of filament
- All of the above
Answer.4. Temperature of filament Explanation:- Choice of material for the filament The materials commonly used as the filament for incandescent lamps are carbon, tantalum, tungsten, and osmium. The materials used for the filament of the incandescent lamp have the following properties. The color temperature of a normal filament lamp is typically between 2800 K and 3000 K. At the extremely high temperature of the filament, tungsten tends to evaporate. This leads to the familiar blackening of an incandescent lamp envelope. The evaporation of the tungsten filament can be reduced by filling the lamp envelope with a suitable gas that does not chemically attack the filament.
Ques.29. A zero watt lamp consumes
- No power
- About 5 to 7 W power
- About 15 to 20 W power
- About 25 to 30 W power
Answer.2. About 5 to 7 W power Explanation:- Zero watt Night Lamp is a Low incident light bulb this bulb requires a very low current i.e around (0.023 A) and the power consumption is also very low 3 – 7 W. In earlier days the analog electric energy meter was not very efficient to sense or measure zero-watt bulb, therefore the meter uses to show zero or no consumption.
Ques.30. Melting temperature of tungsten is
- 2000° K
- 2500° K
- 2655° K
- 3655° K
Answer.2. 3655° K Explanation:- Property of Tungsten