Ques.31. The life of the incandescent lamp is expected to be
- 100 Hours
- 200 Hours
- 1000 Hours
- 10000 Hours
Answer.3. 1000 Hours Explanation:- Incandescent lamps Incandescent lamps have been around for a long time and are still commonly used, but they don’t perform as well as some of the other lamps on the market.
Ques.32. The source of illumination for a cinema projector is
- Incandescent Lamp
- Mercury Vapour Lamp
- Sodium Lamp
- Carbon Arc lamp
Answer.4. Carbon Arc lamp Explanation:- Carbon arcs operate by ionizing air molecules (which carry the current between the carbon electrodes) to incandescence. To ignite the lamp, the rods are touched together, thus allowing a relatively low voltage to strike the arc. The rods are then slowly drawn apart, and electric current heats and maintains an arc across the gap. The tips of the carbon rods are heated and the carbon vaporizes. The carbon vapor in the arc is highly luminous, which is what produces the bright light. The rods are slowly burnt away in use, and the distance between them needs to be regularly adjusted in order to maintain the arc. The carbon arc lamp was mainly used in the cinema projector. A carbon electrode projector produces the best possible light, a pure white with even brightness. But the rods are consumed in less than an hour (another reason for changeovers), and their burning produces carbon monoxide. The carbon-arc played a significant role until the introduction of the short-arc xenon discharge lamp in 1951.
Ques.33. In the case of frosted GLS lamps, the frosting of the shell is done by
- Ozone
- Ammonia
- Acid etching
- Saltwater
Answer.3. Acid Etching Explanation:-
Ques.34. Nitrogen or argon is filled in GLS lamps to
- Reduce the glare
- Improve efficiency
- Change the color of light
- Retard evaporation of tungsten filament
Answer.4. Retard evaporation of tungsten filament Explanation:- INCANDESCENT FILAMENT LAMP These lamps are temperature-dependent sources. When an electric current is made to flow through a fine metallic wire, which is known as the filament, its temperature increases. At low temperatures, it emits only heat energy, but at very high temperatures, the metallic wire emits both heat and light energy. These incandescent lamps are also Blown as temperature radiators. The color temperature of a normal filament lamp is typically between 2800 K and 3000 K. At the extremely high temperature of the filament, tungsten tends to evaporate. This leads to the familiar blackening of an incandescent lamp envelope. The evaporation of the tungsten filament can be reduced by filling the lamp envelope with a suitable gas that does not chemically attack the filament. However, gases also cool the filament by conducting heat away from it, and they decrease lamp efficiency. The gas used must, therefore, be carefully chosen. It should adequately suppress tungsten evaporation without overcooling the filament. In addition, it should not readily pass an electric current, for otherwise arcing may occur which would destroy the lamp. Argon and nitrogen are the gases most commonly used. Nitrogen will minimize the risk of arcing but will absorb more heat than argon. Argon is used by itself in general service lamps. A mixture of the two gases is used in incandescent lamps where the tendency for arcing is more likely, such as in projector lamps. In this case, the amount of nitrogen present is kept very small as little as 5% in order to obtain optimum lamp efficiency. Lamps filled with krypton gas have a longer life than argon and nitrogen lamps and cost more. By using a mixture of nitrogen krypton, this rise in temperature can be overcome, but the excessive cost of Krypton, gas does not make it economically viable. Abundantly available, the cheapest inert gas is nitrogen. It’s the molecular weight being low, it cannot put much pressure on the disintegrating molecules of the tungsten filament, especially at higher voltages. lithe next choice fell on argon which gave three times more life than the nitrogen-filled lamps. The use of pure argon in lamps again brought some difficulty at the higher temperature. Argon molecules in combination with very minute particles of impurities produce electrical discharges between the exposed portion on the filament at the foot of the stem. So, a little amount of nitrogen gas is used to avoid this local action. For higher wattage lamps, 92% argon with 8% nitrogen gas mixture is recommended. For lamps upto 100 watts, the mixture of 86% argon and 14% nitrogen is more economic and efficient too.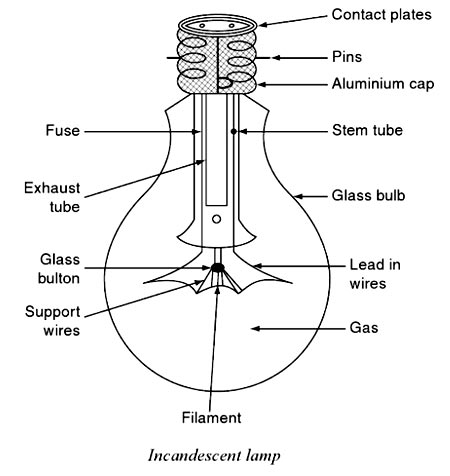
Ques.35. Which of the following lamp has the least capacity to sustain voltage fluctuations?
- Sodium vapor lamp
- Fluorescent lamp
- Incandescent lamp
- Mercury vapor lamp
Answer.3. Incandescent lamp
Explanation:-
Effect of Voltage variation in an incandescent lamp
Whenever the voltage at the terminals of a utilization device valley from the devices nameplate rating, Something is sacrificed in either the life or performance of the equipment. This is certainly true for all types of lamps. For instance, with incandescent lamps, a 1% deviation from rated voltage will cause a change of 3 to 3½% in lumen output. A 10% reduction in lamp voltage will result in a 30% reduction in lumen output; while with an overvoltage of 10%, the lamp life is reduced to one-half of normal. With fluorescent lamps, a 1% variation in the line voltage will change the lumen output by only 1%. Both low and high voltages are undesirable and tend to reduce lamp life and lower lumen maintenance. Mercury lamps (one of the HID lamps) are less sensitive and generally give good performance within ±5% variation in line voltage.
- Filament lamps(Incandescent lamps) are very sensitive to voltage variation.
- A 5% over-voltage halves lamp life due to the over-running of the filament.
- A 5% under-voltage prolongs lamp life but leads to the lamp giving much less than its proper light output while still consuming nearly its rated wattage.
Ques.36. The light output of GLS lamps is normally in the range
- 10 to 18 lumens/watt
- 50 to 80 lumens/watt
- 100 to 180 lumens/watt
- 200 to 300 lumens/watt
Answer.1. 10 to 18 lumens/watt Explanation:- GLS lamps produce light as a result of the heating effect of an electrical current. Most of the electricity goes to producing heat and a little to producing light. A fine tungsten wire is first coiled and coiled again to form the incandescent filament of the GLS lamp. The coiled-coil arrangement reduces filament cooling and increases the light output by allowing the filament to operate at a higher temperature. The light output covers the visible spectrum, giving a warm white to yellow light with a color rendering quality classified as fairly good. The efficacy of the GLS lamp is 10-20 lumens per watt over its intended lifespan of 1000 h.
Ques.37. In neon signs, argon gas is used for
- Yellow color
- Blue color
- Red color
- Green color
Answer.2. Blue Explanation:- Neon signs are electric signs lighted by long luminous gas-discharge tubes that contain rarefied neon or other gases. These are used in advertising, decoration, and for various signs. The tube requires a reactance for liming the current. They are available in various colors depending on the rare gas used. Not all electrified, tubular glass signs “neon” signs contain neon gas. Neon is just one of several gaseous elements used in sign creation. Helium gas, argon gas, mercury vapor, and sodium vapor are also used to make brightly colored signs. Electrified gas tubes are also used to make works of art. Each of these gases glows in a characteristic color, which never changes. When no electrical energy is present, all these elements are colorless in the gas phase. When electricity is added, these elements release energy with wavelengths in the visible range of the electromagnetic spectrum. Neon Gas ⇒ Red Mercury Vapor ⇒ Blue-green Helium Gas ⇒ Pinkish White Sodium Vapor ⇒ Violet Argon Gas ⇒ Bright-Blue
Ques.38. Glare may result from
- Excessive lighting contrast in the field of vision
- Excessive luminance
- Either of (A) or (B) above
- None of the above
Answer.3. Either of (A) or (B) above Explanation:- Glare is a kind of visual noise that interferes with vision. In any discussion of natural light, the problem of glare deserves particular mention, and the reduction of glare is an essential feature of qualitative light planning. Even though areas with elevated brightness draw our attention and can help create an ambiance rich in contrast, luminances that are too high or luminance differences that are too great can severely diminish the perception. Various terms are commonly used to distinguish between glare situations and the way they work. Thus, occurrences of glare are differentiated first according to the way they originate, that is, whether the disruptive ray of light strikes the eye directly or indirectly via a reflecting surface. A bright object alone does not necessarily cause glare, but a bright object in front of a dark background will usually cause it. Direct glare is caused by the light source itself; for example, the sun or a bright part of the sky. The angle of glare is crucial, that is, the angle whose vertex is defined by the eye and whose sides extend to the visual task and the source of glare. This type of glare can be reduced naturally and most easily when light sources (i.e., window openings) are arranged to lie as far as possible from the most frequent line of vision. Glare by reflection, on the other hand, originates indirectly from the reflection of the light source on shiny surfaces. The best-known examples of this are reflections as they occur on bodies of water, glasses, veneers, polishes, but also on glossy paper or on monitors. Glare by reflection can be diminished by reducing the illuminances shining on surfaces or appropriately distributing brightness with light sources that cover large areas and radiate light diffusely.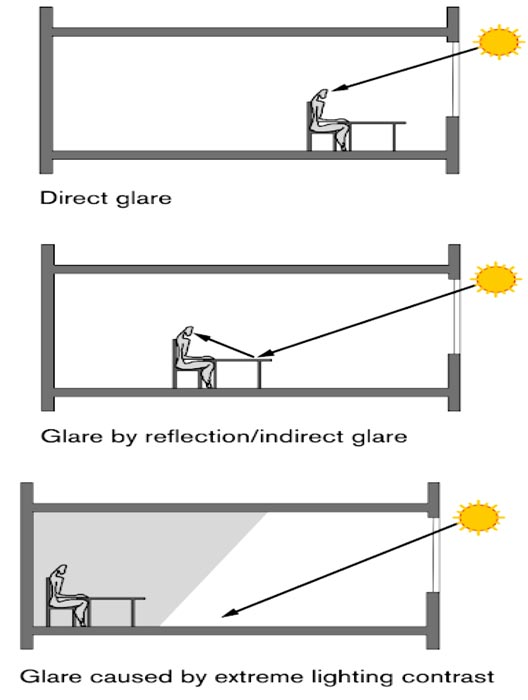
Ques.39. In neon signs, neon with a mixture of mercury gives
- Green color
- Blue color
- Red color
- Yellow color
Answer.3. Red color Explanation:- Noble gases (neon, argon, helium, xenon, and krypton) are mixed with a small amount of mercury to create a particular color. Each gas has a distinctive color. Neon gives a red color; argon enhanced with mercury creates a bright blue; krypton is a yellow-white light.
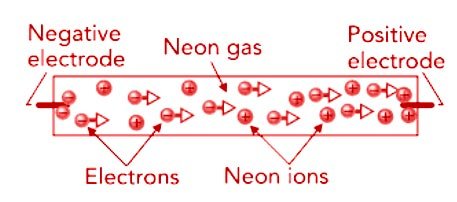
Ques.40. The electrodes of neon tubes work at
- Very low temperatures
- Ordinary voltages
- 400 to 440 volts
- 2000 to 6000 volts
Answer.4. 2000 to 6000 volts Explanation:- Lamps commonly called neon tubes are discharge tubes that contain a low pressure of neon or some other gases that emits visible light. The walls of such tubes are usually clear, so the color seen is the actual color of the gas discharge. Neon tubes generally operate on alternating current (AC), so the two electrodes function as the cathode for different parts of the AC cycle The electrodes are typically iron tubes with an internal coating of alkaline-earth oxides that promotes the emission of electrons, The discharge heats the electrodes to around 300°F (150°C). The power supply to the tube is controlled by a ballast—an electromagnetic or semiconductor device that provides an initial-high voltage “kick” but restricts the current that flows once the gas has ionized and the resistance of the tube has fallen to nearly zero. Without a ballast, the current through the tube could increase uncontrollably, eventually vaporizing the electrodes. While ordinary air breaks down at a voltage gradient of about 30,000 V/cm, low-density neon breaks down at a much lower voltage gradient. That’s because, in a low-density gas, charged particles can travel farther and accumulate more kinetic energy before each collision. When about 10,000 volts is applied between the electrodes of a neon sign tube, the gas breaks down and begins to emit its familiar red glow. The lamp is then experiencing a discharge, that is, current is flowing through the neon gas. This current consists mostly of electrons, flowing from the tube’s negatively charged electrode to its positively charged electrode. While these electrons collide frequently with neon atoms, they have so little mass that they usually just bounce off the atoms without losing much energy. Like a PingPong ball rebounding from an elephant, the electron does most of the bouncing and then continues on its way.Neon lamps