11. Find the output voltage for the squarer circuit given below, choose input frequency as 10kHz and Vref =10v
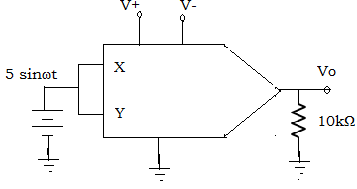
A. Vo = 5.0-(5.0×cos4π×104t)
B. Vo = 2.75-(2.75×cos4π×104t)
C. Vo = 1.25-(1.25×cos4π×104t)
D. None of the mentioned
12. Calculate the phase difference between two input signals applied to a multiplier, if the input signals are Vx= 2sinωt and Vy= 4sin(ωt+θ). (Take Vref= 12v).
A. θ = 1.019
B. θ = 30.626
C. θ = 13.87
D. θ = 45.667
13. Express the output voltage equation of the divider circuit
A. Vo= -(Vref/2)×(Vz/Vx)
B. Vo= -(2×Vref)×(Vz/Vx)
C. Vo= -(Vref)×(Vz/Vx)
D. Vo= -Vref2×(Vz/Vx)
14. Find the input current for the circuit given below.
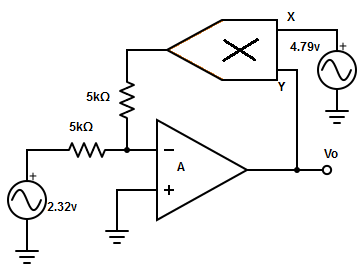
A. IZ = 0.5372mA
B. IZ = 1.581mA
C. IZ = 2.436mA
D. IZ =9.347mA
15. Find the condition at which the output will not saturate?
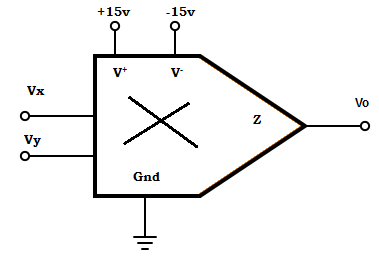
A. Vx > 10v ; Vy > 10v
B. Vx < 10v ; Vy > 10v
C. Vx < 10v ; Vy < 10v
D. Vx > 10v ; Vy < 10v
16. Determine the relationship between log-antilog method.
A. lnVx×lnVy = ln(Vx+Vy)
B. lnVx / lnVy = ln(Vx-Vy)
C. lnVx -lnVy = ln(Vx/Vy)
D. lnVx+ lnVy = ln(Vx×Vy)
17. Which circuit allows doubling the frequency?
A. Frequency doubler
B. Square doubler
C. Double multiplier
D. All of the mentioned
18. Compute the output of the frequency doubler. If the inputs Vx = Vsinωt and Vy = Vision(ωt+θ) are applied to a four-quadrant multiplier?
A. Vo= { Vx×Vy× [cosθ-(cosθ×cos2ωt)+(sinθ×sin2ωt)]}/ Vref
B. Vo= { Vx×Vy× [cosθ-(cosθ×cos2ωt)+(sinθ×sin2ωt)]}/ 2
C. Vo= { Vx×Vy× [cosθ-(cosθ×cos2ωt)+(sinθ×sin2ωt)]}/(2×Vref)
D. Vo= – { Vx×Vy× [cosθ-(cosθ×cos2ωt)+(sinθ×sin2ωt)]}/(2×Vref)
19. How to remove the dc term produced along with the output in the frequency doubler?
A. Use a capacitor between load and output terminal
B. Use a resistor between load and output terminal
C. Use an Inductor between load and output terminal
D. Use a potentiometer between load and output terminal
20. Find the voltage range at which the multiplier can be used as a squarer circuit?
A. 0 – Vin
B. Vref – Vin
C. 0 – Vref
D. All of the mentioned
6. Calculate the output voltage of a squarer circuit, if its input voltage is 3.5v. Assume Vref = 9.67v.
A. 2.86v
B. 1.27v
C. 10v
D. 4.3v
