In which of the milling operation cutter is rotated in the same direction if travel of the workpiece
Right Answer is:
Down milling
SOLUTION
Milling is the process of machining using rotary cutters to remove material by advancing a cutter into a workpiece. A milling machine uses a multipoint tool to remove metal from a workpiece. The use of multipoint tools enables the machine to achieve^fast rates of metal removal and produce a good surface finish.
Types of milling processes
Milling processes may be divided into two types:
- Peripheral milling
- Face Milling
Peripheral milling:-
In this operation, the machined surface is parallel to the axis of rotation of the cutter. Two types of processes are possible, depending on the sense of rotation of the cutter relative to the direction of movement of the workpiece. These processes are termed up milling and down milling.
Up milling is the conventional type of milling in which the cutter is rotated against the direction of travel of the workpiece. The thickness of the chip is small at the beginning and increases towards the end of the cut. The upward cutting force tends to lift the workplace from the table. Due to the nature of the cutting forces, the difficulty is experienced in feeding coolant at the beginning of the cut. In spite of the disadvantages, it is used so often because it is safer. It is particularly useful for milling castings containing particles of sand, and also for milling welded joints.
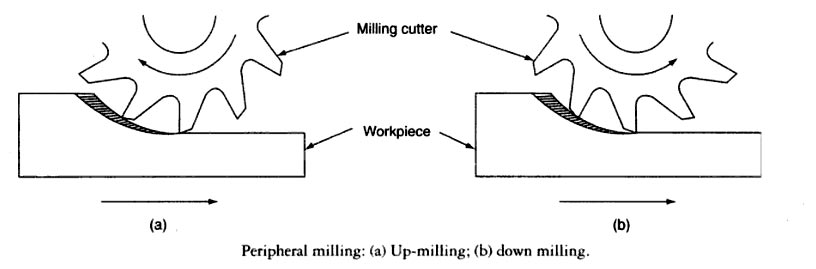
Down milling which is also called climb milling, is a process in which the cutter is rotated in the same direction as the direction of travel of the workpiece. The thickness of the chip and the cutting force is a maximum when the tooth begins cutting, and a minimum when the tooth stops cutting. Here, metal is removed when the cutter moves downwards. In this case, the clamping of the work is easier and the chips are disposed of more easily. Coolants can be fed into the cutting zones, and this reduces heat problems and gives a better surface finish. However, down milling cannot be used on machines having the backlash. The backlash causes the work to be drawn below the cutter at the beginning of the cut and leaves the work free when the cut is over. This results in vibration and damage to the workpiece.
Face milling produces a flat machined surface perpendicular to the axis of rotation of the cutter. The main cutting is done by the peripheral cutting teeth while the face cutting edges finish the work by removing a small quantity of metal.
