1. What is the conversion ratio of the phase detector in 565 PLL?
A. 0.14
B. 0.35
C. 0.4458
D. 0.7
2. Given fo = 1.2kHz and V = 13v, find the lock-in range of the monolithic Phase-Locked Loop.
A. ±575Hz
B. ±720Hz
C. ±150Hz
D. ±1kHz
3. A monolithic phase detector is preferred for critical applications as it is:
A. Independent of variation in amplitude
B. Independent of variation in the duty cycle of the input waveform
C. Independent of variation in response time
D. Both 1 and 2
4. Determine the capture range of IC PLL 565 for a lock-in range of ± 1kHz.
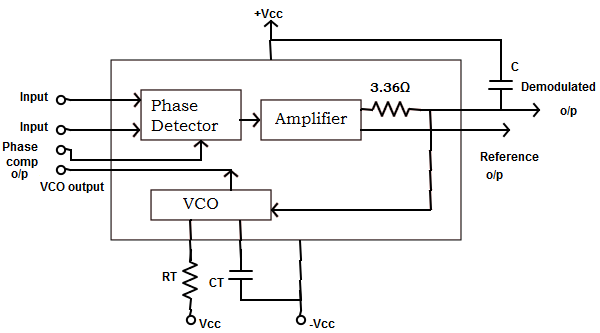
A. △FC = ±31.453Hz
B. △fc = ±66.505Hz
C. △fc = ±87.653Hz
D. None of the mentioned
5. Find the lock-in range of the monolithic Phase-Locked Loop from the given diagram.
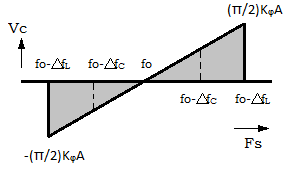
A. -fo-△fL to fo-△fL
B. -fo-△fL to -fo-△fC
C. fo-△fL to fo-△fC
D. -fo-△fC to fo-△fC
6. At what range the PLL can maintain the lock in the circuit?
A. Lock in range
B. Input range
C. Feedback loop range
D. None of the mentioned
7. At which state the phase-locked loop tracks any change in input frequency?
A. Free running state
B. Capture state
C. Phase-locked state
D. All of the mentioned
8. Output current in general-purpose op-amp can be increased using
A. Power comparator
B. Power amplifier
C. Power resistor
D. Power booster
9. Which type of power transistor is chosen for a discrete power booster?
A. Collector follower stage
B. Emitter follower stage
C. Base follower stage
D. None of the mentioned
10. What is the power dissipation of the power transistor?
A. ≅ 0.5W
B. ≤ 0.5W
C. > 0.5W
D. ≠ 0.5W
