11. Find the current flowing between terminals A and B of the circuit shown below.
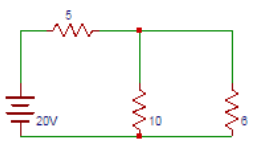
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
Answer: D
The magnitude of the current in Norton’s equivalent circuit is equal to the current passing through the short-circuited terminals that are
I = 20/5 = 4A.
[/bg_collapse]
12. Find the equivalent resistance between terminals A and B of the circuit shown below.

A. 0.33
B. 3.33
C. 33.3
D. 333
13. Find the current through a 6Ω resistor in the circuit shown below.

A. 1
B. 1.43
C. 2
D. 2.43
14. Find the voltage drop across the 6Ω resistor in the circuit shown below.

A. 6.58
B. 7.58
C. 8.58
D. 9.58
15. Find the current flowing between terminals A and B in the following circuit.
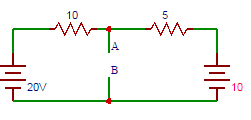
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
Answer: D
Short-circuiting terminals A and B,
20 − 10(I1) = 0
I1 = 2A. 10 − 5(I2)
I2 = 2A.
Current flowing through terminals A and B = 2 + 2 = 4A.
[/bg_collapse]
16. Find the equivalent resistance between terminals A and B in the following circuit.

A. 3
B. 3.03
C. 3.33
D. 3.63
17. Find the current flowing between terminals A and B obtained in the equivalent Nortan’s circuit.

A. 8
B. 9
C. 10
D. 11
Answer: D
To solve for Norton’s current we have to find the current passing through the terminals A and B. Short-circuiting the terminals a and b,
I = 100/(6×10)/(6 + 10) + (15×8)/(15 + 8)) = 11.16 ≅ 11A.
[/bg_collapse]
18. Find the equivalent resistance between terminals A and B obtained in the equivalent Nortan’s circuit.

A. 8
B. 9
C. 10
D. 11
19. Find the current through a 5Ω resistors in the circuit shown below.

A. 7
B. 8
C. 9
D. 10
20. Find the voltage drop across a 5Ω resistor in the circuit shown below.

A. 33
B. 34
C. 35
D. 36
Answer: D
The voltage drop across 5Ω resistor in the circuit is the product of current and resistance
= > V = 5×7.16 = 35.8 ≅ 36V.
[/bg_collapse]
