The graph shown below is related to which type of class in the motor
Right Answer is:
Continuous Duty with constant Load
SOLUTION
Continuous Duty with constant Load
There are two types of continuous duty
- Continuous duty at constant load
- Continuous duty with variable load cycle.
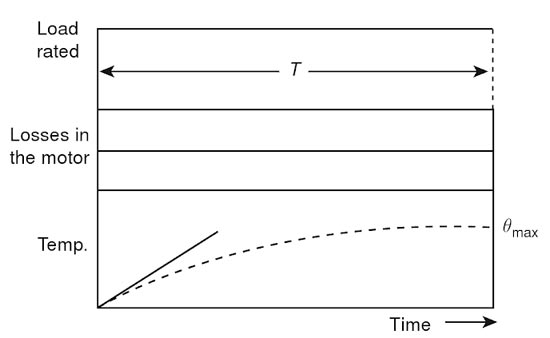
In Continuous duty at constant load, the load torque remains constant for a sufficiently long period corresponding normally to a multiple of the time constant of the drive motor. The drive motor is therefore loaded for a sufficient amount of time continuously, till it attains thermal equilibrium.
While driving such a load a motor should have a rating sufficient to drive it without exceeding the specified temperature. The rating of the motor selected for this duty is called its continuous rating or design rating. By continuous rating, one means that it is the maximum load that the motor can give continuously over a period of time, without exceeding the temperature rise. Also, the motor selected should be able to withstand momentary overloads. Therefore, the selected motor may sometimes have a rating slightly greater than the power required by the load.
The load diagram and the temperature rise curve of the motor selected for the purpose are shown in Fig. Centrifugal pumps, fans, conveyors, and compressors are some types of loads where this type of continuous duty at constant load is required.

The selection of a motor for this class of duty is rather simple and straightforward. From the load characteristics or requirements, one can determine the continuous input required to the mechanical load. A suitable motor may be selected from the catalog of series manufactured motors. The design rating normally takes care of heating and temperature rise and the motor normally has a short time overload capacity.
While selecting a motor for this type of duty it is not necessary to give importance to the heating caused by losses at starting even though they are more than the losses at rated load. This is because the motor does not require frequent starting. It is started only once in its duty cycle and the losses during starting do not have much influence on heating. However, sometimes it may be necessary to check whether the motor has sufficient starting torque if the load has a considerable amount of inertia.
