A reverse voltage of 20 V is across the diode. What is the voltage across the depletion layer?
A reverse voltage of 20 V is across the diode. What is the voltage across the depletion layer?
Right Answer is:
20 V
SOLUTION
- When the positive terminal of a dc source or battery is connected to the n-type and the negative terminal is connected to the p-type semiconductor of a PN junction, as shown in Fig.. the junction is said to be in reverse bias.
- As the barrier potential is increased, it is very difficult for the majority carriers (holes in the P-type region and electrons in the N-type region) to diffuse across the junction.
- In this case, the applied reverse potential acts in such a way that it establishes an electric field which increases the field due to the potential barrier. Thus, the barrier potential at the junction is strengthened.
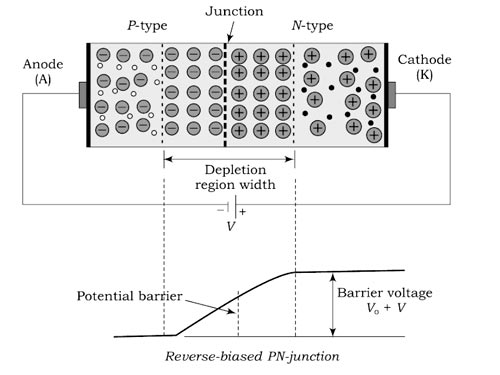
- When the holes and electrons move away from the junction, the newly created ions increase the difference of potential across the depletion layer.
- The wider the depletion layer, the greater the difference of potential. The depletion layer stops growing when its difference of potential equals the applied reverse voltage.
- When this happens, electrons and holes stop moving away from the junction.
Since in reverse bias, the resultant field is strengthed i.e (electric field + potential barrier), but we can’t measure the voltage across the potential barrier hence the total voltage across the depletion layer is equal to the applied electric field i.e 20 V
