Ques.51. Assertion (A): A hot wire ammeter has a cramped scale
Reason (R): The heat is proportional to the square of the current
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true but R is false
- A is false but R is true
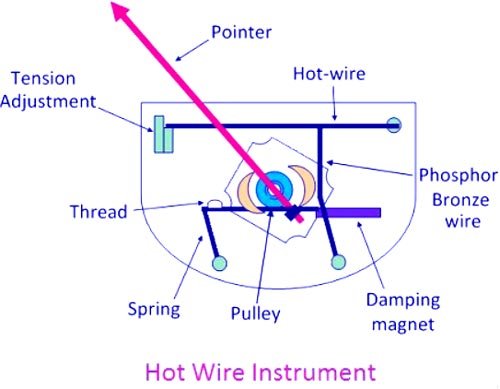
Answer.1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A Explanation:- The working of the hot-wire instrument is based on the heating effect of electric currents. When the current to be measured passes through the hot wire, the wire gets heated and then expands. Since the wire is fixed between two points, it sags due to expansion which is magnified by the phosphor-bronze wire and silk thread. This expansion is taken up by the spring and the silk thread, which causes the pulley to rotate and the pointer is deflected. Deflecting Torque The deflection of the pointer of the hot-wire instrument is proportional to the extension of the hot wire, which is itself proportional to the square of the current. Hence Deflecting Torque. Td ∝ I2 If spring control is used, then Controlling torque Tc ∝ θ (deflection) For balanced condition TC = Td ∴ θ ∝ I2 Thus, these instruments have a square-law type scale. They read the r.m.s value of current and are independent of its frequency. Since the deflection of the pointer is proportional to the square of the current flowing through the coil. The scale of the instrument is, therefore. a cramped scale (NON-LINEAR) i.e. there will be congestion at the beginning of the scale. Working Of Hot Wire Instrument
Ques.52. The standard one color unit is equivalent to
- 1 mg/l cobalt chloride
- 1 mg/l platinum cobalt
- 1 mg/l platinum chloride
- 1 mg/l cobalt sulfate
Answer.2. 1 mg/l platinum cobalt Explanation:- The color intensity of liquids may be estimated rapidly by using platinum-cobalt standards. This method is particularly applicable to those materials in which the color-producing substances have light-absorption characteristics nearly identical with those in the standards. Colors having hues other than light yellow or reddish yellow cannot be determined with these standards. The platinum cobalt color standards contain carefully controlled amounts of potassium chloroplatinate and cobaltous chloride. Each platinum cobalt color unit is equivalent to 1 mg of platinum per liter of solution (1 ppm), and the standards are named accordingly. For example, the No. 20 platinum- It standard contains 20 ppm of platinum. These platinum-cobalt standards are also called APHA (American Public Health Association and Hazen standards).
Ques.53. The fluoride concentration less than prescribed permissible limit may cause
- Dental cavities
- Spotting in teeth
- Discoloration of teeth
- Fluorosis
Answer.1. Dental cavities Explanation:- Fluoride is a natural element found in the earth landmass and, in varying amounts, in all water: Fluoride protects teeth from decay in two: During tooth formation fluoride is incorporated into the tooth structure, making it more resistant to decay(referred to as systematic fluoride.) After tooth eruption, fluoride remineralizes areas of file tooth that have been demineralized (referred to as topical fluoride). A fluoride concentration level greater than the permissible limit poses a threat to human health. The most prominent health-related problem due to excess fluoride is mainly dental caries, teeth mottling, endemic cumulative fluorosis causing skeletal damage and deformation to children and adult.
Ques.54. The ultrafine particle present in surface water is removed through
- Coagulation and flocculation
- Filtration
- Sedimentation
- Reverse osmosis
Answer.1. Coagulation and flocculation Explanation:- External Treatment of Water External water treatment includes the following steps: filtration, chlorination, clarification, softening, precipitation, ion exchange, de-alkalization, demineralization, deaeration, and reverse osmosis (RO). Filtration:- Filtration removes or minimizes such impurities as coarse suspended matter, silt, clay, and some organic materials. It also removes floc or sludge produced by coagulation or softening. Filtration is a mechanical process and therefore does not remove dissolved solids. Undissolved solid particles in water are removed by using either gravity filters or pressure filters. Filtration also removes the rust particles formed due to corrosion in the boiler and steam piping or tubing. Coarse suspended matter in water is removed by using gravity or pressure filters. However, when the suspended solids are very fine, clarification of the solution using a coagulation and flocculation step is mandatory to ensure effective filtration. Clarification:- The objective of clarification is to remove suspended matter and color from water. The term clarification is used in connection with the turbidity in water. High-purity water is colorless and completely transparent. However, raw water used in boilers is not normally high purity and has several suspended impurities in it, which makes it turbid. Lack of clarity in water is referred to as turbidity. The suspended particles range from a few microns in diameter to the submicron and nano levels with a high surface area. They usually have a net negative charge on their surface, which keeps them in suspension in a medium such as water (as the like charges on the neighboring particles’ surfaces repel them from each other). Clarification is a process of removal of such insoluble suspended impurities from water and consists of steps including coagulation and flocculation. Coagulation:- Because ultra-fine-sized suspended solid particles are present in raw water, cartridge filters are at times unable to filter them. In such a situation, the water is treated before filtration with chemicals known as coagulants, and the treatment is known as coagulation. It is a process of neutralization of the negative charges from the surface of the fine particles, which makes them unite to one another by providing a nucleus to form masses or agglomerates that can be filtered. Chemicals such as alum (aluminum sulfate), sodium aluminate, ferric sulfate, ferric chloride, activated silica, and high-molecular-weight polyelectrolytes are often used as coagulants. They cause impurities that are otherwise present as fine suspensions in the solution to settle. Hard and high-TDS water is treated more easily than soft and low-TDS water. Flocculation:- Stable agglomerates of small particles are converted into large floes by a process called flocculation. This is done by stirring or gentle agitation of a coagulated solution. Flocs, by virtue of their higher specific gravity, tend to settle at the bottom. The clear water is then separated from the floes by Recantation.
Ques.55. The pollutant lead present in the atmosphere may cause
- Respiratory disease
- Asthmatic disease
- Cardiovascular disease
- Pulmonary edema
Answer.3. Cardiovascular disease Explanation:- Heavy metals most commonly associated with harmful effects in humans include lead, mercury, arsenic, and cadmium. Lead (Pb) is a heavy toxic metal, it may be found in hazardous concentrations in food, water, and air and it is one of the most common overexposures found in the industry. The organ systems most affected by lead include the nervous hematopoietic, reproductive, gastrointestinal, cardiovascular, and musculoskeletal systems as well as the kidneys. Exposure occurs through inhalation, ingestion, and uncommon skin contact. Lead is taken in through direct contact with the mouth, nose, and eyes (i.e., mucous membranes); and through cuts in the skin. Inorganic lead, found in the most common sources of paint, food, and consumer products, is only minimally absorbable through the skin. The absorption of inorganic lead is primarily from ingestion and inhalation. Most of the absorbed lead (80% to 85%) is incorporated into bone and teeth where it competes with calcium; the half-life in bone is 20 to 30 years. Lead can move from bone to the bloodstream years after the initial exposure. Children store about 70% of absorbed lead in their bones and teeth; thus, other tissues in children are more greatly affected compared to adults.
Ques.56. A continuous exposure to intense noise for a longer duration may cause irreversible damage to the nerves and the inner ear resulting in loss sensitivity at higher frequencies which is called
- Acoustic trauma
- Annoyance
- Temporary threshold shift
- Permanent threshold shift
Answer.4. Permanent threshold shift Explanation:- High noise levels, at least, lead to Temporary Threshold Shif (TTS) which are dependent on the preceding exposure and last for varying time periods. After repeated exposures to noises that initially cause only TTS, a worker may experience threshold changes that do not recover. This is called a noise-induced permanent threshold shift. Permanent threshold shift results from prolonged exposure to loud noise and is irreversible due to the permanent reduction in nerve impulses to the brain. This shift is most marked at the 4000 Hz frequency, which can lead to difficulty in hearing certain consonants and some female voices. It is important to note that, if the level of noise exposure remains unchanged, noise-induced hearing loss will lead to a permanent threshold shift affecting an increasing number of frequencies. The hearing loss caused can be temporary or permanent.
Ques.57. The presence of CO2 may reduce the pH of rainwater up to
- 5.6
- 4.0
- 6.5
- 6.0
Answer.1. 5.6 Explanation:- All rainwater is mildly acidic because ionization of at atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) that dissolves in it produces a solution with a pH of approximately 5-6 (compared with a neutral pH = 7.0. The acidity produced by CO2 can be significantly increased by the solution of sulfur and nitrogen oxides (SO2 and NO2). The pH of rainwater can range from quite acidic around 4.0 in industrial regions to about 5.6 in very clean regions. When water moves through the subsurface, it equilibrates with soil gases and may become more acidic because of a higher soil concentration of dissolved CO2. Acidic groundwater has an increased capacity for dissolving minerals. The higher the CO2 concentration in soil air, the lower is the pH of groundwater.
Ques.58. Plotter is an
- Input device
- Output device
- Storage device
- Both input and output device
Answer.2. Output device Explanation:- A plotter is a pen-based output device that is attached to a computer for making vector graphics, that is, images created by a series of many straight lines. It is used to draw high-resolution charts, graphs, blueprints, maps, circuit diagrams, and other line-based diagrams. It is similar to the printer, but it draws lines using a pen. As a result, it can produce continuous lines, whereas the printer can only simulate lines by printing a closely spaced series of dots. Multicolor plotter uses different-colored pens to draw different colors. Color plots can be made by using four pens (cyan, magenta, yellow, and black) and need no human intervention to change them.
Ques.59. DVD stands for
- Digital video Disk
- Digital Variable Disk
- Digital Versatile Disk
- Digital Versatile Data
Answer.3. Digital Versatile Disk Explanation:- DVD stands for Digital Versatile Disk
Ques.60. Which of the following can be treated as both input as well as output devices?
- Mouse
- Printer
- Memory
- Plotter
Answer.3. Memory Explanation:- I/O Device (Peripherals) The device that gives information to the computer is called an input device. For example, keyboard, mouse, joystick, microphone, A/D converters are all input devices. The device that receives information from the computer is called an output device. For example, LED, LCD, monitor, printer, speaker, D/A converter are output devices. In addition to input devices and output devices, some devices function as both input and output devices. The I/O devices provide the input to the computer as well as get output from the computer. The I/O devices are used by both the input unit and the output unit. Hard disk drives, floppy disk drives, optical disk drives are examples of I/O devices. Memory such as Floppy drive, CD-RW (reader/writer) is input as well as output devices.



