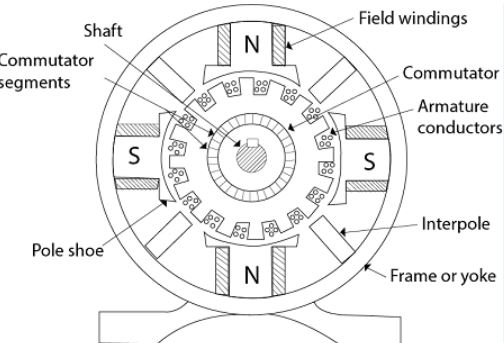
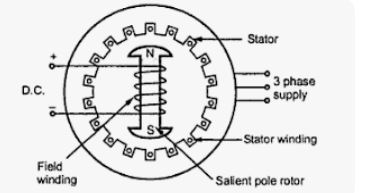
On the basis of winding arrangement
On the basis of winding arrangements, transformers are classified into one type i.e Auto Transformer
In Auto Transformer, one single winding is used as primary winding as well as secondary winding i.e primary and secondary shares the common single winding. The primary is electrically connected to the secondary, as well as magnetically coupled to it.
Transformer based on usage
The transformers are used to do many functions depending upon the application they have. These are classified as
⇒Power transformer
⇒Distribution transformer
⇒Protection transformer
⇒Measuring transformer
Power transformer
- The power transformer is used for high power transfer application.
- It is used for the step up and steps down application where the transmission voltage is greater than 33KV and are generally rated above 200MVA.
- Higher flux density.
- Higher level of insulation
- Used for the transmission and distribution of electric power.
- Power transformer can be used in furnace and welding machine.

Example of power transformer
Laminated core transformers, stray leakage transformers, variable auto transformers, polyphase transformers etc.
NOTE- Power transformer should be designed to have maximum efficiency at near or full load.
Advantages of power transformer
- Low noise
- Higher efficiency
- High Insulation level
- High power application
Application of power transformers
- Used in transmission substations.
- It is used in the high voltage transmission network to step up and step down the voltage.
- used in power generation systems.
Distribution transformers
- It is used for distribution of electric energy at low voltage to end user level.
- For the industrial purpose, the operating voltage is around 33 KV.
- For the domestic purpose, the operating voltage is around 220 – 440 Volts.
- The efficiency of a distribution transformer is around 50 – 70{e3f30b17d1e2ee29a456ac094afcdceaab760d87d11dd966225a50cd59ff675b}, which is low as compared to the power transformer.
- Smaller in size as compared to the power transformer.

Example of distribution transformer
Oil-cooled transformers, three phase auto transformers.
NOTE- Distribution transformer should be designed to have maximum efficiency at a load much lower than full load (about 50 percent)
Advantages of distribution transformer
- Easy in installation.
- Small in size.
- Low magnetic losses.
Disadvantages of distribution transformer
- They are not fully loaded.
- Efficiency is low.
Application of distribution transformer
- Used for distribution of electricity in house, farms, industries, railways etc.
Instrument Transformer
The instrument transformers are used for measuring high voltage and high currents in Ac Systems. It measures electrical quantities such as voltage, current, frequency, power factor etc.
Types of Instrument Transformer
Instrument transformer are of two types:-
- Current transformer
- Voltage transformer
Current Transformer (C.T)
- Current transformers are generally used to measure currents of high magnitude.
- The current transformer is used to step down the current to a lower value so that current can be measured with a normal range ammeter.
- The current transformer has a primary coil of one or more turns of thick wire connected in series.
- The secondary coil consists of a large number of turns of fine wire and it is connected across the ammeter terminals.
- Therefore current transformer steps up the voltage while stepping down the current.
- A current transformer is always connected in series.
Potential transformer
- Potential transformers are also known as voltage transformers.
- Potential transformers are generally used to measure voltages of high magnitude.
- Potential transformers are used to step down the voltage to a lower value so that voltage can be measured with a small range voltmeter.
- The primary of voltage transformer has a large number of turns connected across the line of the voltage.
- The secondary voltage transformer consists of few turns and it is connected directly to a voltmeter.
- The voltage transformer is always connected in parallel.