Ques.121. Which of the following radioactive byproducts releases from nuclear reaction?
- Cesium
- Tritium
- Strontium
- All of these✓
The radioactive byproducts releases from nuclear reaction are
Ques.122. Which of the following DC generator is employed in ARC welding?
- Shunt
- Cumulative
- Series
- Differential Compound✓
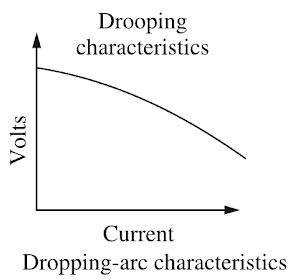
Arc welding is the widely used method of joining the metal parts. Here the source of heat is an electric arc. Arc welding is a group of welding processes wherein heating is produced with an electric arc or arcs, mostly without the application of pressure and with or without the use of fillet metal, depending upon the base plate thickness. ARC Welding Principle In arc welding, the ARC is generated between the positive pole of D.C. (direct current) called anode and the negative pole of D.C. called cathode. When these two poles are brought together, and separated for a small distance (1.5 to 3 mm) such that the current continues to flow through a path of ionized particles, called plasma, an electric arc is formed. Since the resistance of this ionized gas column is high, so more ions will flow from anode to the cathode. Heat is generated as the ions strike the cathode. A.C. or D.C. Machines in ARC Welding Depending upon the application, A.C. or D.C. machines are used in arc welding, but in some cases, either of them can be used. D.C. supply is usually obtained from generators driven by electric motor or if no electricity is available then diesel engine can be used. D.C. welding is mostly used for heavy work and at sites where electricity is not available. Arc welding requires a power source that can deliver electrical power at low voltage and high current such that it can establish and sustain an arc plasma column between the welding electrode and the workpiece. The line voltage in the mains supply is too high to be used directly in arc welding. Therefore either a transformer, solid-state inverter/rectifier or a motor-generator set is used to obtain the required open circuit voltage necessary for arc welding. It is generally in the range of 20-80 V. At the same time the same power source should be capable of delivering high current typically ranging from 50 to 1500 A. This welding power source can have the output of alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC). These power sources have volt-ampere characteristics typically of constant current (CC) or constant potential (CP) type. The output may also have a pulsing mode. A schematic of the basic elements of an arc welding power source is shown in Fig. An arc behaves in a totally different manner from a norms resistance. As the current is increased the potential drop across the arc, instead of increasing as with an ohmic resistance, decreases up to a current of the order of 50-70 A, and then become approximately constant. This is because with increasing current arc increases in size, allowing a larger area for curve flow, and also increases in temperature becoming thereby more conducting. The generator used for welding purposes should have high current and low voltage which can be obtained by the differential compound generator. Differentially compounded DC generator has drooping characteristics that mean if load current increases the net flux will decreases(i.e shunt field and series fields in opposition will increases)due to demagnetization effect hence the Induced EMF and terminal voltage decreases.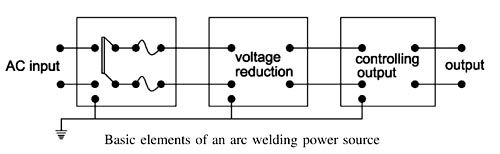
Ques.123. Which of the following power plants requires the largest area to produce the same amount of electricity?
- Diesel power plant
- Nuclear power plant
- Solar Power Plant✓
- Thermal Power Plant
A solar-thermal power plant uses solar radiation to produce high-temperature heat that drives a heat engine cycle to produce electrical energy. Solar thermal power plants use reflectors and collectors to concentrate the sunlight onto a small area, which significantly enhances the temperature. The heat is collected by a working fluid and is coupled to a heat exchanger to drive a vapor power cycle. Solar thermal power plants have been confined to desert areas, with a high fraction of sunny, cloudless days. The installed, worldwide capacity is small, approximately 400 MW and the amount of electric energy generated annually is about I TWh. Solar-thermal systems can also produce hot water and steam for industrial applications. Advantages and disadvantages of solar power Some of the advantages of converting solar energy into electric power are: Disadvantages One of the greatest disadvantages of photovoltaic systems is the large area of land required for electric power generation. Solar energy is a diffuse energy resource: 3 to 10 km2 is required for a 100 MW plant, with the total amount of electricity generated per year being 180 GWh/y compared to an equivalent annual energy production from a 30 MW thermal power plant and a land area of about 0.01 km2. However, incorporation of solar photovoltaic systems into rooftops and other building materials can essentially eliminate the land requirements and provide distributed generation at the point of demand.
Ques.124. Which of the following generator is used in conjunction with turbines in a hydropower plant?
- Wound Rotor Induction Generator
- Salient pole Synchronous generator✓
- Squirrel cage Induction Motor
- Cylindrical core synchronous Generator
Ques.125. Which of the following is the Curie temperature (in Kelvin) of Iron (Fe)?
- 948
- 713
- 1043✓
- 858
In physics and materials science, the Curie temperature (TC), or Curie point, is the temperature above which certain materials lose their permanent magnetic properties, to be replaced by induced magnetism. Curie temperature of Iron is 1043 K. The Curie temperature is an essential temperature for a ferromagnetic material. For example, if a ferromagnetic material has a temperature under its Curie temperature, then the material has a net spontaneous magnetization, which means that the material becomes ferromagnetic, or magnetic. If a ferromagnetic material has a temperature over its Curie temperature, then the material becomes paramagnetic or does not become a magnet.
Ques.126. Which one is the schematic arrangement of the steam power station?
- Coal and ash handling, steam generating plant, steam turbine, alternator, feed water, the cooling arrangement✓
- Steam generating plant, steam turbine, feed water, alternate, cooling arrangement
- Cooling arrangement, feed water, alternator, steam generating plant, coal and ash handling
- All of these
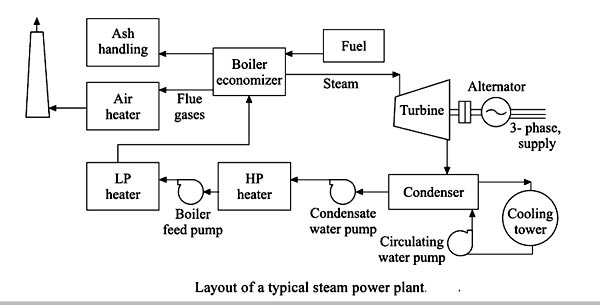
The steam power plant is also called as the thermal power plant. It is the important source to produce the electricity. In thermal power plants, steam is generated by heating the water and is used to rotate the turbines which are coupled with the synchronous generators (also known as alternators) to produce electricity. Steam can be generated from coal, gas or nuclear as the main fuel. Coal, which is the main fuel used in thermal power plants, is fired in the boiler to generate heat for producing steam. The thermal efficiency of a steam power plant mainly depends on the choice of the steam cycle and varies from 28% to 35%. The principal equipment of steam power plants is the boiler, super-heater, feed water pump, steam reheater, condenser, turbine, and generator. The major components of the steam generating plants are shown in Figure. In large thermal power plant unit, several stages of turbines such as high pressure, intermediate pressure and low pressure are used to extract more power from the steam and thus, to increase the efficiency of the machine with minimum cost. For generating the electricity using the steam turbine, high-speed synchronous generators are used because the efficiency of steam turbines is high at high speed. Since the speed of turbo alternator is high, the diameters of the machine are kept minimum so that the centrifugal fort acting on the rotor is minimized. To keep the same electrical loading (which is proportional area x length), the length of the turbo-alternators is increased. General arrangement of the Steam power plant:- The various constituents of steam power station can be divided into the following stages Fuel and Ash circuit In the steam power plant, the coal is used as a fuel. The coal is stored in a coal store plant the storage helps to supply the coal continuously. Then the coal is transferred to the coal handling plant where the coal is pulverized i.e. crushed into small pieces. Such a crushed coal is transferred to the boiler from the coal handling plant. Steam Generating Circuit The main component of the steam generating circuit is the boiler. But much other auxiliary equipment is used so as to completely utilize the heat of flue gases. 1. Boiler: The boiler is a closed vessel where water is converted to the steam using th heat of the coal combustion. Hence the boiler is called steam generator. 2. Superheater: It is an accessory attached to the boiler and located in the path of flue gases leaving the boiler and flowing towards the chimney. By using the heat of the flue gases the superheater converts the wet steam into superheated dry steam. 3. Economizer: It is another accessory attached to the boiler and located in the path of flue gases. Thus it utilizes the heat of flue gases which would otherwise be wasted to the atmosphere. The water from the feed pump is passed through the economizer to the boiler drum so that before entering the boiler, it is heated and hence less efforts are required to convert it into steam. This increases the overall boiler efficiency, saves the fuel and reduces the stress on the boiler. Steam Turbine The dry and superheated steam from the superheater is supplied to the turbine. The heat energy of He steam is converted to He mechanical energy as steam passes over the turbine blades. There are two types of steam prune movers available, steam engine and steam turbine. The steam turbine is practically used because of the following advantages. i) High efficiency ii) Simple construction iii) Low maintenance iv) High-speed v) Less floor area vi) No flywheel required vii) Le~ problems of vibrations Alternator The alternator shaft is coupled to the turbine. When the turbine shaft rotates, the alternator shaft rotates and it converts the mechanical energy into an electrical energy. Feed Water Circuit The condensate leaving the condenser is used as the feed water. Because it goes to the boiler, it is fiat heated in a dosed feedwater heater. Then * is passed to economize where it is further heated and then passed to the boiler. This increases the overall efficiency of the plant. The feed water source is generally a river or a canal. It contains suspended and dissolved impurities. Cooling Water Circuit For improving the plant efficiency, the expanded steam coming out of the turbine passes through the condenser where it is condensed into water. The condenser is very important as it creates a very low pressure at the exhaust of the turbine the help in the expansion of steam in the turbine at low pressure.
Ques.127. Which one of the following is not the part of a steam power plant?
- Prime Mover
- Condenser
- Water Treatment Plant
- None of these✓
Ques.128. Which one acts as a mechanical rectifier in the process of converting AC current into DC current where the EMF is induced in the armature winding?
- Rheostat
- Rotor
- Commutator✓
- Stator
The commutator is one of very important part of dc machine which rotates with the armature. The function of the commutator is to convert alternating currents induced in the armature conductors into direct currents in the external circuit in case of generator operation. In the case of a dc motor, the function of the commutator is to produce a unidirectional torque. The commutator also helps to keep the magnetic flux stationary in space. Generally, the alternating voltage is produced in the coil, which is rotating in a magnetic field, but the direct current is required in the external circuit. For this purpose, the commutator is needed. Each commutator segment is connected to the ends of the armature coils. The commutator receives the current from the brushes, which are also placed on the rotating armature.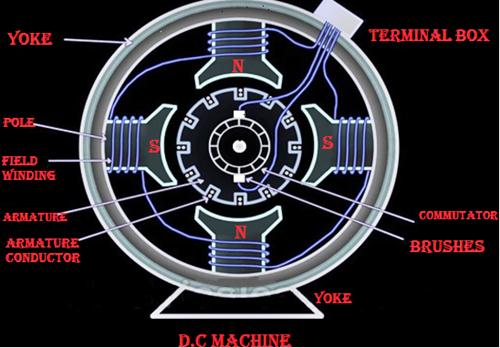
Ques.129. Which one of the following device is used as a protection against lightning?
- Surge diverters
- Overhead ground wires
- Earthing screen
- All of these✓
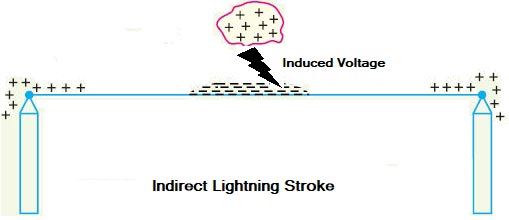
Types of Lightning Strokes There are two main types of lightning strokes that appear on various equipment in the power system. They are viz. Direct Stroke and Indirect Stroke. Direct stroke may appear on line conductor, on tower top or on the ground wire indirect stroke may appear on overhead line conductors. Direct Stroke on Overhead Conductors These strokes are most dangerous as their effects are most severe and harmful. In this type of stroke, the discharge or the current path is directly from the cloud to the overhead line. From the line, the current path may be over the insulators down the pole to the ground. The voltage set up is in millions which can cause flashover and puncture of insulators. The insulators may get shattered till the surge is sufficiently dissipated and it travels to both sides. The wave may reach to the substation and damage the equipment because of excessive stress produced. The earthing screen and the ground wire provide protection against direct lightning strokes but do not provide any protection against travailing waves which may reach the electrical apparatus. The lightning arresters or the surge arresters are the ones who provide protection against the travailing waves. Indirect Strokes The effect of indirect strokes is similar to that of direct strokes. Their effect is more severe in case of distribution lines than in case of high voltage lines. These strokes are due to electrostatically induced charges on the conductors due to the presence of charged clouds. Sometimes currents may be induced electromagnetically due to lightning discharge in the immediate vicinity of the line which results in an indirect stroke. Following method can be employed for the protection of the device from the lightning stroke, Overhead ground wire or earth wire:- Earth wire is also called as the guard wire and it mainly protects lines from lightning. If in case lightning struck then it carries the excessive current inrush to ground. Its radius is much smaller than the actual transmission wire because as the resistance is inversely proportional to an area of cross-section and as the cross-section decreases, the resistance increases. The increased resistance of earth wire is able to withstand high inrush of current caused due to lightning and it will safely guide this inrush into the ground. It is placed above all the conductors mainly because if lightning struck then it will strike at the uppermost point in the line configuration and protect the actual conductors. Surge absorber or Surge diverter:- The surge absorber and surge diverters are types of overvoltage protection which limit the transient overvoltage and switching overvoltages. The steepness of wavefront of traveling waves can cause damage to the apparatus in addition to the magnitude of the wave. More steeper is the traveling wave, the damage to the apparatus is more. Thus to reduce the steepness of wavefront of the surge, surge absorber is used. Earthing Screen:- It consists of a network of copper conductors (generally caned shield or screen) mounted all over the electrical equipment in the substation or power station. The shield is properly connected to earth on atleast two points through a low impedance. The power station & sub-station can be protected against direct lightning strokes by providing earthing screens. On the occurrence of the direct stroke on the station, the screen provides a low resistance path by which lightning surge are conducted to ground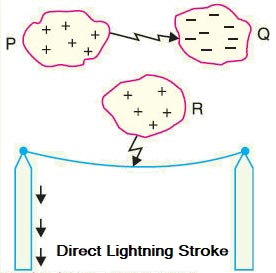
Ques.130. The law of electromagnetic induction is also called:-
- Joule’s law
- Faraday’s law✓
- Coulomb’s law
- Ohm’s Law



