11. The input voltage, 6v, and reference voltage, 4 v are applied to a log-amp with saturation current and temperature compensation. Find the output voltage of the log-amp?
A. 6.314(kT/q)v
B. 0.597(kT/q)v
C. 0.405(kT/q)v
D. 1.214(kT/q)v
12. Determine the output voltage for the given circuit
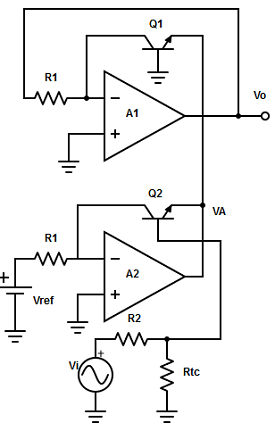
A. VO = Vref/(10-k’vi)
B. VO = Vref+(10-k’vi)
C. VO = Vref×(10-k’vi)
D. VO = Vref-(10-k’vi)
13. Calculate the base voltage of the Q2 transistor in the log-amp using two op-amps?
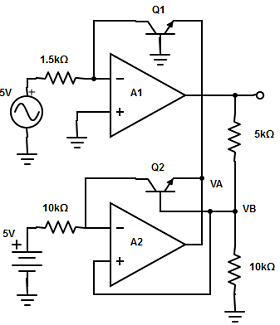
A. 8.7v
B. 5.3v
C. 3.3v
D. 6.2v
14. Determine output voltage of analog multiplier provided with two input signals Vx and Vy.
A. Vo = (Vx ×Vx) / Vy
B. Vo = (Vx ×Vy / Vref
C. Vo = (Vy ×Vy) / Vx
D. Vo = (Vx ×Vy) / Vref2
15. Match the List-I with list-II
| List-I | List-II |
| 1. One quadrant multiplier | i. Input 1- Positive, Input 2- Either positive or negative |
| 2. Two quadrant multiplier | ii. Input 1- Positive, Input 2 – Positive |
| 3. Four quadrant multiplier | iii. Input 1- Either positive or negative, Input 2- Either positive or negative |
A. 1-ii, 2-i, 3-iii
B. 1-ii, 2-ii, 3-ii
C. 1-iii, 2-I, 3-ii
D. 1-I, 2-iii, 3-i
16. What is the disadvantage of the log-antilog multiplier?
A. Provides four-quadrant multiplication only
B. Provides one quadrant multiplication only
C. Provides two and four-quadrant multiplication only
D. Provides one, two, and four-quadrant multiplication only
17. An input of Vsinωt is applied to an ideal frequency doubler. Compute its output voltage?
A. Vo = [(Vx×Vy) /Vref2] × [1-cos2ωt/2].
B. Vo = [(Vx2×Vy2) /Vref] × [1-cos2ωt/2].
C. Vo = [(Vx×Vy)2 /Vref] × [1-cos2ωt/2].
D. Vo = [(Vx×Vy) /( Vref] × [1-cos2ωt/2].
18. Find the output voltage for the squarer circuit given below, choose input frequency as 10kHz and Vref =10v
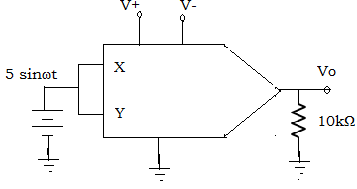
A. Vo = 5.0-(5.0×cos4π×104t)
B. Vo = 2.75-(2.75×cos4π×104t)
C. Vo = 1.25-(1.25×cos4π×104t)
D. None of the mentioned
19. Calculate the phase difference between two input signals applied to a multiplier, if the input signals are Vx= 2sinωt and Vy= 4sin(ωt+θ). (Take Vref= 12v).
A. θ = 1.019
B. θ = 30.626
C. θ = 13.87
D. θ = 45.667
20. Express the output voltage equation of the divider circuit
A. Vo= -(Vref/2)×(Vz/Vx)
B. Vo= -(2×Vref)×(Vz/Vx)
C. Vo= -(Vref)×(Vz/Vx)
D. Vo= -Vref2×(Vz/Vx)
