100 Most Important MCQ on Electric Drive | Industrial Drive MCQ | Objective Type Question Electric Drive with Explanation- 2021
Ques 1. The consideration involved in the selection of the type of electric drive for a particular application depends upon
- Speed control range and its nature
- Starting Nature
- Environmental condition
- All of the above
Answer.4. All of the above Explanation:- Motor control is required in a large number of industrial and domestic applications such as transportation systems, rolling mills, paper machines, textile mills, machine tools, fans, pumps, robots, and washing machines. Systems employed for motion control are called drives and may employ any of the prime movers. Drives employing electric motors are known as electric drives. or The system which is used for controlling the motion of an electrical machine, such type of system is called an electrical drive. Factors Affecting the Selection of Electric Drive The selection of electric drives basically means the selection of drive motors. Following are the various factors that influence the selection of motor to drive the load:
Ques 2. Which of the following motor is preferred for automatic drives?
- Ward Leonard controlled dc motors
- Squirrel cage induction motor
- Synchronous motors
- Shunt Motor
Answer 1. Ward Leonard controlled dc motors Explanation: The Ward-Leonard system consists of a fixed speed 3-phase AC induction motor driving by a separately excited DC generator that, in turn, feeds a variable voltage to a shunt wound DC motor. So this is essentially a DC variable speed drive. The basic principle of the DC variable speed drive is that the speed of a separately excited DC motor is directly proportional to the voltage applied to the armature of the DC motor. The main changes over the years have been concerned with the different methods of generating the variable DC voltage from the 3-phase AC supply. Ward Leonard control of dc machines is considered one of the most elegant and efficient methods of speed control over a wide range. The schematic diagram of the control technique is shown in Figure. The system consists of a separately excited generator feeding power to the dc motor to be controlled. The generator, “G” is driven at a constant speed by an ac motor connected to the ac mains. The driving motor may be an induction motor or a synchronous motor. Where ac mains are not available, a diesel engine or a gas turbine acts as a prime mover to run the generator. This generator drives a motor ‘ M”. The motors “G” and ‘ M” must be of equal rating. Adjusting the field current of the generator, the motor terminal voltage can be controlled. The field winding voltage of the generator can be smoothly varied in either direction. Therefore, the motor terminal voltage and the speed of the motor can be varied smoothly from full negative to full positive. Modern installations use thyristor converter circuit for variable voltage dc supply. One of the advantages of Ward Leonard drive system is its ability for regenerative braking, thereby delivering power to the grid, corresponding to low motor speeds. For regenerative braking, the output voltage of generator “G” is reduced below the induced voltage of the motor “M” by decreasing the generator field excitation. This reverses the current flow in the armature of the machines “G” and “M”. As the current is reversed, the machine “G” will act as a motor and the machine “M” will act as a generator. The mechanical energy supplied to the machine “M” is converted into electrical energy; which is now supplied to the machine “G’ [presently working as a motor]. The machine “G” will act as a prime mover for the ac machine which will now work as generator feeding power to the grid. The nature of the speed-torque characteristic is similar to that shown in Figure. Drop in motor speed due to change in load torque is caused by Iara drop in both the machines. When the generator output voltage is high, the motor speed is automatically high. The Iara drop in both machines will be negligible compared to their outputs. Therefore, the % speed regulation of the motor will be excellent. The Ward Leonard drive is used in steel rolling mills, paper plants, elevators, machine tools. Nowadays, static Ward-Leonard drives, using two thyristor bridge rectifiers (converters) connected back to back, are used to eliminate the above drawbacks. More precise and smooth speed control over a wide range such as 200:1, and even higher, is accomplished in which there are no sources of noise and vibration. In such an adjustable voltage system, higher torque-speed characteristics can be obtained by providing id compensation. Soft starting can also be incorporated. Non-electrical prime movers can be used to drive the dc generator of the Ward-Leonard drive. For example, in diesel-electric locomotives and ship propulsion drives, the generator is driven by a diesel engine or a gas turbine. Examples of applications are rolling mills, paper mills, mine hoists, etc.Ward Leonard Speed Control
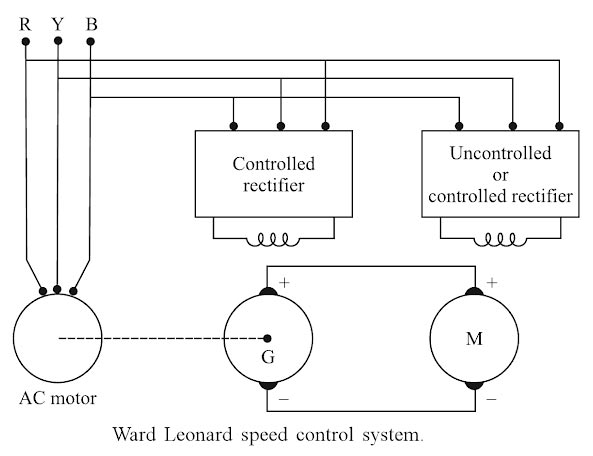
The main advantages of Ward Leonard scheme are:
The main disadvantages of Ward Leonard scheme are:
Ques 3. The consideration involved in the selection of the type of electric drive for the Load Variation application depends upon
- Constant Load
- Continuous Variable Load
- Pulsating Load
- All of the above
Answer.4. All of the above Explanation:- Selection of Motor based on Load Variation While selecting a motor it is necessary to consider the variation of load torque with speed and time. This is related to the torque rating of the motor i.e. how much and what type of torque motor can produce safely. The variation of load torque with speed basically decides the type of motor to be selected. While the variation of load torque with time decides the rating of the motor to be selected. Such a factor that influences the selection of rating of the motor based on the load variation with time is called the load variation factor. One cycle of variation of the load is called a duty cycle. The different types of load variations with time and corresponding examples of load are given below:
e.g. fan type loads, paper making machines etc.
e.g metal cutting lathes, conveyors, etc
e.g. reciprocating pumps, compressors, all loads having Bank shaft.
e.g rolling vanilla, presses, sharing machines, forging hammers
e.g. all forms of cranes, hoist, elevators.
e.g. motor-generator sets for charging batteries, household equipment.
Ques 4. __________ drive is also called as Line shaft drive
- Individual drive
- Multimotor drive
- Group Drive
- None of the above
Answer 3. Group Drive Explanation:- CLASSIFICATION OF ELECTRICAL DRIVES Electrical drives may be grouped into the following three cate^lpriee: Group drive:- A drive in which a single electric motor drives a line shaft by means of which an entire group of working machines may be operated is called group drive. It is also sometimes called as the line shaft drive. The line shaft is fitted with multi-stepped pulleys and belts that connect these pulleys and the shafts of the driven machines serve to vary their speed.
Ques 5. The advantages of a group driver electric drive are
- HIgh efficiency
- Low Noise
- Constant speed
- All of the above
Answer 1. High Efficiency Explanation:- Advantages of Group driver electric drive Saving in the initial cost: One 150 kW motor costs much less than ten 15 kW motors required to drive 10 separate machined High Efficiency:- The efficiency and power factor of a large group drive motor will be higher, provided it is operated fairly near its rated load. High Overload capacity:- If the machines are liable to short but sharp overloads, group drive is again advantageous, because 100 percent overload on an individual machine will cause hardly 10 percent overload when driven by group drive. Continous start and stop:- Group drive can be used with advantage in those industrial processes where there is the sequence of continuity in operation and where it is desirable to stop these processes simultaneously as in a flour mill.
Ques 6. The disadvantages of group drive electric machine is/are
- Low efficiency
- Low overload capacity
- Can’t be used for constant operation
- All of the above
Answer 3. Can’t be used for constant operation Explanation:- Disadvantages of Group driver electric drive Group drive is adopted, when existing factories are changed from engine drive to electric motor drive simply by replacing the oil or steam engine by an electric motor of corresponding output retaining all the old shafts and belts.
belts) and is less safe to operate.
pulleys, belts, etc.
idle.
the position of the line shaft.
Ques 7. In __________ drive each machine is driven by its own separate motor with the help of gears and pulley
- Individual drive
- Multimotor drive
- Group Drive
- None of the above
Answer 1. Individual Drive Explanation:- Individual drive. In “individual drive”, each machine is driven by its own separate motor with the help of gears, pulley etc.
Examples: Single-spindle drilling machines, various types of electrical hand tools and simple types of metal working machine tools and mechanisms.
Ques 8. The advantages of the individual drive is/are
- Flexibility in operation
- Each machine can be run or stop as desired
- Maintenance of Lineshaft, the bearing is eliminated
- All of the above
Answer 4. All of the above Explanation:- Advantages of Individual Drive Disadvantage. The only disadvantage of the individual drive is its high cost.
Ques 9. The drive which is used for metal-cutting machines tools, rolling mills etc. are
- Individual drive
- Multimotor drive
- Group Drive
- None of the above
Answer 2. Multimotor drive Explanation:- Multimotor drive:- In “multi-motor drives” separate motors are provided for actuating different parts of the driven mechanism. Such a drive is essential in complicated metal-cutting machine tools, paper making machines, rolling mills, etc. The use of individual drives and multi-motor drives has led to the introduction of automation in production processes which, apart from increasing the productivity of various undertakings, has enhanced the reliability and safety of operation.
Example: In traveling cranes, three motors are used: one for hoisting, another for long travel motion, and third for cross travel motion.
Ques 10. What is the total annual cost of a group drive with a motor costing Rs.18000 with that of 10 individual motors, each costing Rs. 5000. The annual consumption is 80000 kWh. Electrical energy costs 20 paise per kWh. Depreciation, maintenance, and other fixed charges amount to 10 percent.
- Rs. 16800
- Rs.1800
- Rs. 18000
- Rs. 17800
Answer.4. Rs 17800 Explanation:- ⇒ The capital cost of group drive = Rs.18000 ⇒ Annual Depreciation, maintenance, and other fixed charges = 10% i.e 10% of 18000 = 18000 × 10 ⁄ 100 = Rs. 1800 Energy consumption per annum = 80000 kWh Annual energy charges = 0.20 × 80000 = Rs. 16000 Total annual cost of Group drive = Annual fixed charge + Annual energy charge = 1800 + 16000 = Rs. 17800.00



