Ques 30. The speed-torque characteristic of a repulsion induction motor is similar to that of a D.C
- Series Motor
- Compound Motor
- Shunt Motor
- None of the above
Explanation:
A repulsion motor operates on the principle that magnetic poles repel each other, not on the principle of a rotating magnetic field. The stator of a repulsion motor contains only a run winding very similar to that used in the split-phase motor.
Repulsion Induction Motor
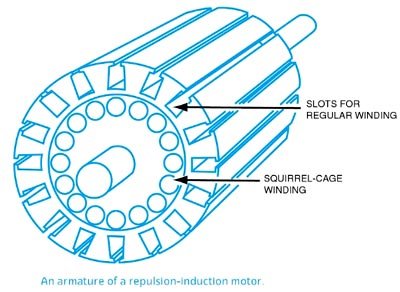
It works on the combined principle of repulsion and induction. The construction of the stator of this type of motor is similar to that of a repulsion motor, i.e., the main stator winding of a single-phase induction motor. In the rotor, there are two separate windings. One winding is similar to the rotor winding of a repulsion motor i.e usual d.c winding connected to the commutator. The other winding is of squirrel-cage type, placed below the repulsion-motor type winding. The behavior of the repulsion induction motor is, therefore, the combination of the behavior of the repulsion motor and an induction motor.
Under starting conditions, very little current will flow through the inner squirrel-cage winding since the reactance of the squirrel-cage winding which is placed deep into the rotor slot is very high. As the rotor picks up speed, the frequency of the rotor induced emf and hence the rotor reactance will decrease. More current will flow in the rotor squirrel-cage winding. The motor will work as a combination of repulsion and induction motor.
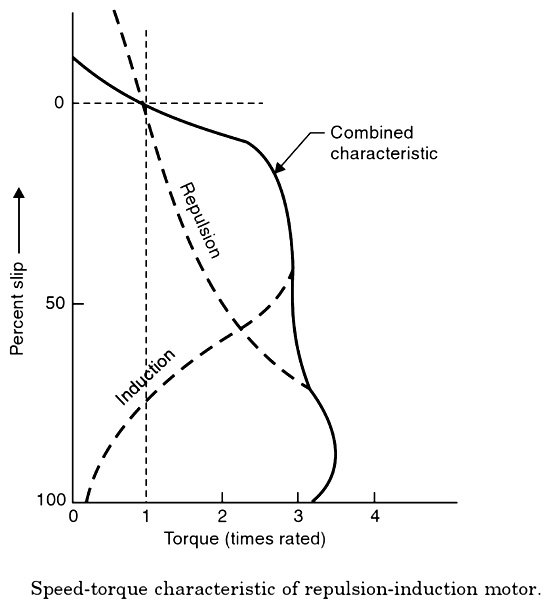
Speed-torque characteristic of a repulsion induction motor
The starting torque repulsion induction motor is 2.25 to 3 times the full-load torque and the starting current will be 3 to 4 times the full-load current. The single-phase repulsion-induction motor has the advantages of high starting torque and good speed regulation. It has the ability to continue to develop torque under sudden heavy applied loads.
The starting torque of the repulsion induction motor is high and it provides fairly constant speed regulation, therefore, its torque-speed characteristics closely resemble DC compound motor.
Ques 31. In a ceiling fan employing capacitor run motor
- Primary winding surrounds the secondary winding
- Secondary winding surrounds the primary winding
- Either 1 or 2
- None of the above
Explanation:
- There are two windings in the ceiling fan, one is running winding and another is starting winding. Two capacitors in parallel are used in domestic ceiling fans. Such a fan’s induction motor is known as a “Two value capacitor run motor”.
- In a ceiling fan, 2 capacitors are used and both are connected in parallel. One capacitor called starting capacitor is connected in series to starting winding and the second is called running capacitor is connected with running winding. The value of starting capacitor is 3 times to value of the running capacitor.
- After the motor reaches 75% of its full load value, the high-value capacitance i.e starting capacitance is disconnected from the circuit and remains in the circuit. This way both optimum starting and running performance is achieved.
- In a ceiling fan, the secondary winding surrounds the primary winding because it improves magnetic locking between stator and rotor and reduces the leakage flux in the winding.
Ques 32. The rotor slots, in an induction motor, are usually not quite parallel to the shaft because
- Improve power factor
- Improve efficiency
- Reducing the tendency of the rotor teeth to remain under the stator teeth
- None of the above
The rotor bars are not exactly parallel to the shaft but are given a slight skew. This skew helps to make the motor run quietly by reducing the magnetic hum. Another advantage is that this skew reduces the locking tendency of the rotor.
Rotor conductors are skewed because of the following main reasons
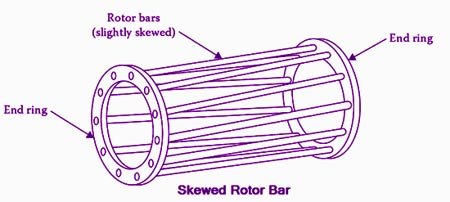
- Cogging:- Cogging is magnetic locking. When an induction motor refuses to start even if full voltage is applied to it, this is called as cogging. This happens when the rotor slots and stator slots are the same in number or they are integer multiples of each other. due to this the opposite poles of the stator and rotor come in front of each other and get locked. Skewing the rotor bars prevents the locking thus preventing Cogging.
- Starting torque of an induction motor depends on the product of the magnitude of stator and rotor current and sine of the angle between both.
- If the conductors remain linear, the angle between stator and rotor current will be 180 degrees. As sin(180)=0, the starting resultant torque will be zero and thus motor will fail to start. This phenomenon is called cogging.
- Skewing helps the motor run more quietly because the magnetic fields are slightly skewed to offset alignment with the rotor field coils. This feature tends to reduce vibration or magnetic hum as the rotor speed changes slightly every time the conductor bars align with the rotor magnetic field. As the speed is the function of frequency so the induction motor is unable to attend the resonance frequency, therefore, the magnetic vibration is reduced.
- Skewing makes the rotor conductor longer with the reduced cross area. This increases the rotor conductor resistance hence starting performance and the torque of an induction motor is improved.
Crawling:– Crawling is a phenomenon where harmonic components introduce oscillations in torque. With the bar skewed, the amount of the bar cutting the field line grows continuously and the next bar starts cutting the field lines as the first finishes. Due to this, we get Uniform Torque.
Ques 33. The motor used for the compressors is
- Reluctance motor
- Shaded pole motor
- DC series motor
- Capacitor start capacitor run motor
Explanation:
In capacitor start capacitor run motor the starting winding and capacitor are connected in the circuit at all times, therefore, the combination of both the capacitor provide higher starting torque and can be used for belt-driven motor such and compressor.
| Single-phase motor | Application |
| Split phase motor | Small drill presses, Shop grinders, Small belt-driven conveyors, Washing machine, |
| Capacitor run induction motor | Compressors, Conveyors, Refrigerators, Air conditioners, Ceiling fans |
| Shaded pole motor | Hairdryers, Toys, Record players, Small fans, Electric clocks |
| AC series motor (universal motor) | Sewing machines, Kitchen applications, Table fans, Food Mixers, Vacuum cleaner |
Ques 34. Starting winding of a single-phase motor of a refrigerator is disconnected from the circuit by means of
- Magnetic Relay
- Centrifugal switch
- Thermal Relay
- None of the above
Explanation:
Electromagnetic relay in Split phase Induction motor
Starting relay
The function of starting relay provided in the refrigerator is to start the split-phase induction motor by connecting the auxiliary winding or starting winding across the main supply in addition to the main winding at the time of starting. This helps to make the split-phase induction motor as the self-induction motor is unable to start.
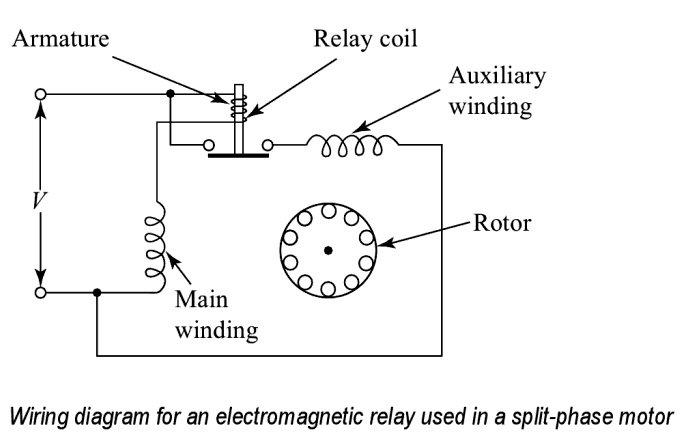
During starting the relay picks up due to high starting current and connects the auxiliary winding in the circuit. When the motor reaches normal speed, current drops to normal value and the electromagnetic relay is dropped and therefore the auxiliary winding gets disconnected from the supply.
In Refrigerator the motor is a single voltage non-reversible type that means the direction cannot be reversed unless the motor is taken apart and the leads of the starting winding are reversed. Therefore instead of a centrifugal switch magnetic relay is used to disconnect the start winding when the motor reaches 75% of its rated speed.
Ques 35. If a single-phase induction motor runs slower than normal, the most likely defect is
- Short circuit winding
- Open circuit winding
- Worn bearing
- All of the above
Explanation:
Causes of the slow speed of induction motor:
Following are the causes due to that speed of induction motor is slow:
- Increase in load
- Worn bearing
- Incorrect coupling of shaft
- Wrong alignment of the shaft motor
- Low supply voltage
Worn bearing: Bearing wear is another common fault in electric motors. As the motor ages, the bearing will change shape due to an imbalance of the motor or just fragmentation of the bearing itself. These deformations cause vibrations that increases the friction between shaft and motor, this will rise in temperature and decreases the speed of the motor as the rotor turns and eventually contribute to failures in other parts of the motor.
Shorted running winding: When running winding is shirted then excessive current is flow and the motor will burn.
Open starting winding: When starting winding of the induction motor is open then the motor is not started.
Insulation failure:- Insulation failure of the motor windings is a common incipient fault in electric motors. The windings of a motor are insulated to prevent shorting of the winding turns. This insulation is categorized into several classes which are rated for different maximum operating temperatures.
Improper fuses: Due to improper fuses, the motor is not started.
Note: Ball bearings reduce friction in machinery by presenting a minimal surface area
Many worn wheel bearings make noise and also decrease speed
Ques 36. In a universal motor, the most common cause of brush sparking is
- Open armature winding
- Shorted armature winding
- High commutator mica
- All of the above
Explanation:
The carbon brush is a crucial piece to keep machines operating efficiently. One common problem is sparking at the brush face, which is usually the first symptom of trouble elsewhere.
Following is a brief rundown of the more common causes of sparking
High commutator mica
If the commutator has high mica or fins of mica that reach up to the brush surface, vibration and sparking may result. Similarly, any burrs of copper left as a result of the undercutting operation will cause trouble. In some locations and atmospheres, commutator slots may become filled with foreign material. This can cause the brushes to vibrate or cause ring fire by permitting current to leak through from one bar to the other.
Open Armature Winding
An open circuit in an armature coil causes “the most vicious form of sparking, which is always accompanied by severe pitting of the mica between the commutator bars connected to this coil and the adjacent coil. The armature must be kept clean to ensure proper balance. Unbalance in the set will pound out the bearings and wear the bearing housing oversize.
Shorted Armature Winding
Shorted armature winding causes excessive arching, lower speed, and loss of power. A short circuit between two sections of a coil, two coils in the same slot, end connections of two coils, or between the commutator bars, will be evidenced by excessive heating of the coils affected, and unless repaired will sooner or later result in a burned-out coil. Blow out the armature regularly with clean, dry compressed air. Clean out the inside of the armature thoroughly by attaching a long pipe to the compressed air line and reaching into the armature coils.
Brush Holders not equally spaced
This condition may appear as unequal sparking on different holders. It can be determined by counting the number of bars between holders or by putting a band of paper around the commutator, marking the positions of the brush toes, removing the paper, and measuring the distance marks.
Brush Holders damaged or dirty
Any physical damage to the holder or an accumulation of dirt on its inside may interfere with the free movement of the brush in the holder and thus result in sparking. Since the commutator is seldom perfectly round or concentric, the brush must move in and out of its holder in order to maintain effective contact.
Overloads
Excessive overloads may result in severe sparking, especially if the interpoles have passed their saturation point and are, therefore, unable to increase their strength as required. If the machine has an ammeter, compare its load with the nameplate rating.
Troubleshooting Universal, Series, Shunt, or Compound DC Motor
| Trouble | Problem cause |
| Will not start | Open circuit in connection to the line.
Open circuit in the motor winding. Worn brushes and/or annealed brush springs. Open circuit or short circuit in the armature winding. |
| Starts, but heats rapidly | Winding short-circuited or grounded. |
| Starts, but runs too hot. | Winding short-circuited or grounded. |
| Sluggish; sparks severely at the brushes | High mica between commutator bars.
Dirty commutator or commutator is out of round. Worn brushes or annealed brush springs. Open circuit or short circuit in the armature winding. Oil-soaked brushes. |
| Abnormally high speed; sparks severely at the brushes. | Open circuit in the shunt winding. |
| Reduction in power; motor gets too hot | Open circuit or short circuit in the armature windings.
Sticky or tight bearings. Interference between the stationary and rotating members. |
| Motor blows fuse or does not stop when the switch is turned to OFF position. | Grounded near switch end of the winding.
Shorted or grounded armature winding. |
| Jerky operation, severe vibration. | High mica between commutator bars.
Dirty commutator or commutator is out of found. Worn brushes and/or annealed brush springs. Open circuit or short circuit in the armature winding. Shorted or grounded armature winding. |
Ques 37. If starting winding of a single-phase induction motor is left in the circuit, it will
- Damage to the starting winding
- Run Faster
- Run slower
- Spark at light load
Explanation:
- In a split-phase induction motor, the starting winding has a relatively small number of tums of fine wire.
- Consequently, its resistance is higher than that of the main winding.
- Owing to the fine wire used on the starting winding. the current density is high and the winding heats up quickly.
- If the starting period lasts for more than 5 seconds, the winding begins to smoke and may burn out unless the motor is protected by a built-in thermal relay.
- Therefore, the split-phase motor incorporates a means of disconnecting the start winding from the supply when the motor has reached sufficient speed.
- A typical method is with a centrifugal switch mechanism that opens a contact and disconnects the start winding from the supply when the motor is around 75 percent of its rated speed.
Ques 38. Most of the fractional horsepower motors have either
- Ball-bearing
- Porous bearing
- Plain or sleeve bearing
- Any of the above
Explanation:
- A fractional horsepower motor (FHP) is an electric motor with a rated output power of 746 Watts or less.
- The term ‘fractional‘ indicates that the motor often has a power rating smaller than one horsepower.
- Plain bearing or sleeve bearing is used in this type of motor because it is the simplest type of bearing, comprising just a bearing surface and no rolling elements.
- Plain bearings, in general, are the least expensive type of bearing. They are also compact and lightweight, and they have a high load-carrying capacity.
Type of bearing
There are two main categories of bearings. The first is known as “plain” or “sleeve” bearings. The second type is “rolling element” bearings. The most familiar type of rolling-element bearing is probably the ball bearing.
Plain or Sleeve Bearings
Plain bearings have no moving parts and depend on a continuous thin film of oil to keep the surfaces from making contact. Most equipment we encounter uses plain bearings. Plain bearings are lubricated with oil, never with grease.
There are some types of plain bearings that do not require lubrication. One type is known as Oilite bearings (pronounced Oil-light). Oilite bearings are made of porous cast bronze impregnated with oil at the factory. The oil contained in the metal is slowly released to the bearing surface and is designed to last the lifetime of the equipment. Oilite bearings do not need to be re-lubricated. Many fractional horsepower motors and other types of small equipment use Oilite bearings.
Other bearings are known as “self-lubricated” and are made of materials that can slide easily without needing additional lubricants. A few of the more common types are Teflon (PTFE), graphite or molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) bonded with epoxy resins, graphite, powdered metal, or ceramics. Lubricating these materials with oil can actually cause damage to the bearing.
Ques 39. Which of the following statements regarding reluctance-start motor is incorrect?
- It is similar to reluctance motor
- Its working principle is similar to shaded pole motor
- The air gap between the rotor and salient poles is non-uniform
- It is an induction motor and not a synchronous one
Explanation:
Reluctance Start Motor
The stator of a reluctance start motor is constructed with salient poles. The starting torque is achieved by creating a non-uniform air gap of the salient poles. Each pole is excited by its own winding carrying the same current. The rotor is usually a squirrel cage type. A reluctance motor is basically a single-phase induction motor.
Reluctance Motor
The three-phase as well as single-phase motors can be built with rotors without DC excitation but having non-uniform air-gap reluctance. The stator construction of such motors is similar to 3-phase or 1-phase induction motors but the shape of the squirrel cage rotor of these motors is changed such that it has variable magnetic reluctance along the air gap. The 3-phase induction motors with such rotors are usually called synchronous induction motors. However, the single-phase induction motors built with a variable air-gap reluctance rotor without DC excitation are called reluctance motors. Reluctance Motor and Hysteresis motor are single-phase synchronous motors.
Note:- A reluctance motor is a single-phase induction motor while Reluctance Motor is single-phase synchronous motors
Ques 40. Which of the following motors have two separate windings on the motor?
- Repulsion start induction run motor
- Repulsion motor
- Repulsion induction motor
- Capacitor start motor
Explanation:
Repulsion Induction Motor
It works on the combined principle of repulsion and induction. The construction of the stator of this type of motor is similar to that of a repulsion motor, i.e., the main stator winding of a single-phase induction motor. The repulsion induction motor is also known as the squirrel cage repulsion motor. In the rotor, there are two separate windings. One winding is similar to the rotor winding of a repulsion motor i.e usual d.c winding connected to the commutator. The other winding is of squirrel-cage type, placed below the repulsion-motor type winding. The behavior of the repulsion induction motor is, therefore, the combination of the behavior of the repulsion motor and an induction motor.
Under starting conditions, very little current will flow through the inner squirrel-cage winding since the reactance of the squirrel-cage winding which is placed deep into the rotor slot is very high. As the rotor picks up speed, the frequency of the rotor induced emf and hence the rotor reactance will decrease. More current will flow in the rotor squirrel-cage winding. The motor will work as a combination of repulsion and induction motor.




